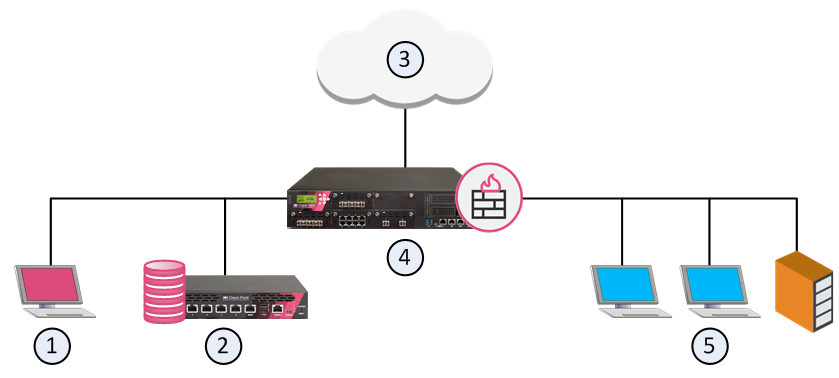
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | SmartConsoleClosed |
| 2 | Security Management Server |
| 3 | Internet and external networks |
| 4 | Security Gateway (Security Group) |
| 5 | Internal network |
|
|
Standalone cell
|
Network Deployment cell
|
|---|---|---|
| Configuration: | Set up each standalone server node through the Profile Management Tool or the zpmt command. Set up additional servers within the node through the administrative console or scripting. | Set up each deployment manager node through the Profile Management Tool or the zpmt command. Add application server nodes to the Network Deployment cell through the Profile Management Tool or the zpmt command. |
| Address spaces: | Minimum: four (location service daemon, controller, servant, control region adjunct) | Minimum: seven (location service daemon, application server controller, application server servant, application server control region adjunct, deployment manager controller, deployment manager servant, node agent) |
| Maximum: Limited only by resources. | Maximum: Limited only by resources. | |
| Administrative isolation: | Each standalone server node is a separate administrative domain. | All nodes in the cell are in the same administrative domain. |
| Operational isolation: | You can start and stop servers independently. Each server has an independent, unshared JNDI namespace. | You can start and stop servers independently. The JNDI namespace is shared among all servers in the cell. |
| Application servers allowed to have multiple servants? | Yes | Yes |
| Clustering available? | No | Yes |
| Bitmap checkpoint | Image checkpoint |
|---|---|
| Bitmap checkpoint can be defined as the process of checking only a part of a particular image. | Image checkpoint can be defined as the process of checking the whole image at a time. |
| Image checkpoint checks the properties of application or image as a bitmap | It is used to check the properties of a Web image. |
| The bitmap can only be used in a defined area. | Image checkpoint can only be used on the whole image and not on any definite part. |
| PORT | TYPE | SERVICE DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
|
18209 |
tcp |
NGX Gateways <> ICAs (status, issue, or revoke) |
|
18210 |
tcp |
Pulls Certificates from ICA. |
|
18211 |
Tcp |
Used by cpd daemon (on the gateway) to receive certificates. |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| No. | 'No.' Refers to the rule number and indicates how important it is. A rule with a higher criticality is assigned a higher place in the Rule Base. |
| Hits | The number of connections for each rule match. |
| Source | Network object that initiates the communication. |
| Destination | Network object which completes the communication. |
| Action | Firewall action is taken when traffic matches a rule. |
| Automatic NAT | Manual NAT |
|---|---|
| 1. Firewalls automatically create the Automatic NAT. | 1. Network Security Administrator manually creates the Manual NAT. |
| 2. We cannot modify the Automatic NAT. | 2. We can modify the Manual NAT. |
| 3. We cannot create Dual NAT. | 3. We can create Dual NAT. |
| 4. In Automatic NAT, port forwarding is not possible. | 4. In Manual NAT, we can do part forwarding. |
Sources : Cisco, and more..