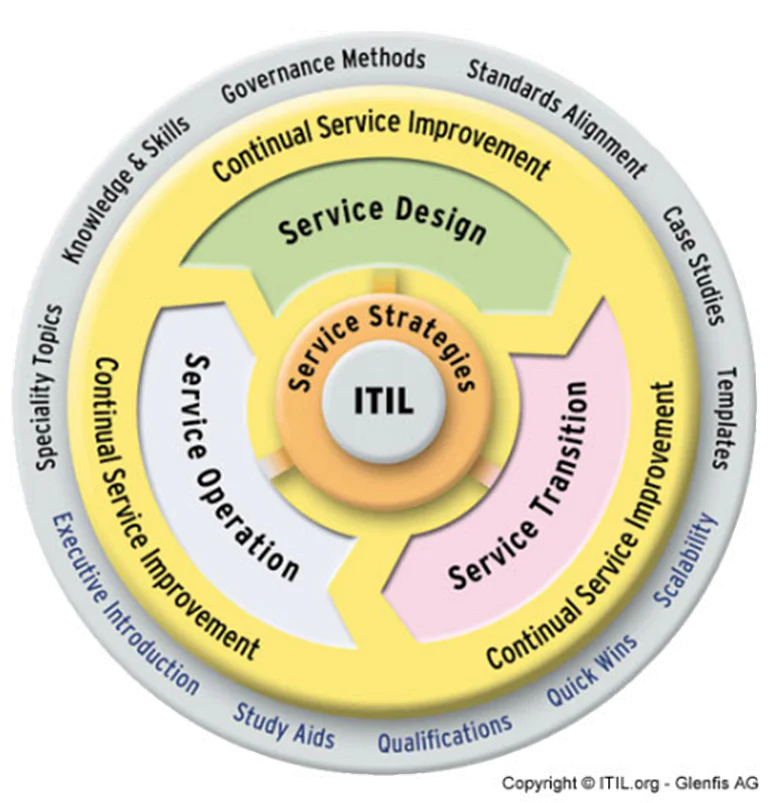
The service value system describes the different components and activities that synergize to create value. These include inputs, elements, outputs, and other components that are relevant to service management.
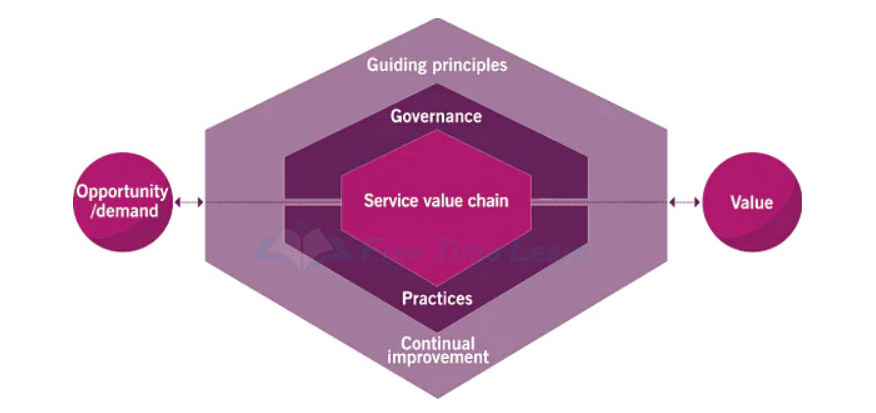
Guiding principles : These are recommendations that can help an organization in any scenario, regardless of the aim, goal, strategy, type of work, management, or structure.
Governance : It offers a structure that’ll help the organization establish and maintain control over its direction. It aims every investment the organization makes to create value and to ensure that they meet business objectives.
Service Value Chain : It is a model used for creating, delivering, and continually improving services. It involves six activities, all of which can be combined in different ways to create multiple value streams.
Practices : These are a collection of organizational resources that focus on performing some specific work or on fulfilling an objective.
Continual Improvement : Focuses on the improvement by improving the service’s effectiveness and efficiency, reducing the cost of services, resources, and other IT management practices.
Opportunity/Demand : Opportunity refers to the organization's options to deliver value to its stakeholders and improve. Demand refers to the need/ desire for products among internal and external customers.