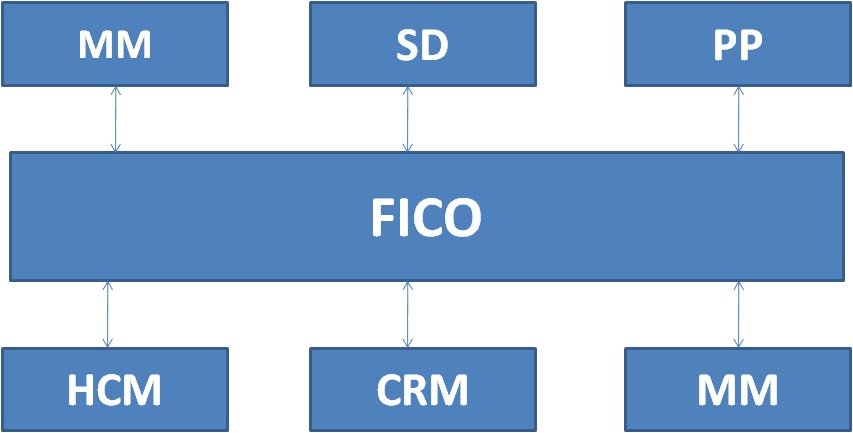
SAP FI enables organizations to make financial statements for reporting and analysis. Types of financial statements may include balance sheets or profit and loss statements. SAP FI consists of several sub-modules that handle specific accounting processes :
* General Ledger contains all of the company's transaction data in a chart of accounts. This lists all of the accounts in the system. Transactions are recorded in sub-modules that can be recorded in real time with general ledger data.
* Accounts Receivable captures customer transactions and manages customer accounts. Transactions include invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payments or executing customer reports.
* Accounts Payable involves all of the transactions with vendors and managed vendor accounts. Transactions can include invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payments, automatic payments program, and executing vendor reports.
* Asset Accounting manages all of the transactions related to the company's fixed assets, such as land, buildings and heavy equipment. Transactions include asset acquisitions, retirement, sales, transfers, revaluations and depreciation.
* Bank Ledger deals with all of the company's bank account transactions and data. It can reconcile all transactions recorded on bank statements and compare them with the transactions in the system.
* Consolidation enables the company to combine financial statements for multiple entities, which provides an overview of the company's financial position as a whole.
* Funds Management manages the budgets for the company's revenues and expenses.
* Special Purpose Ledger defines the ledgers in SAP FI for reporting purposes.
* Travel Management manages all of the transactions for travel processes, including booking trips and handling travel-related expenses.