A computer is an electronic device that processes data according to a set of instructions called a program. It takes input, processes it, stores it, and produces output.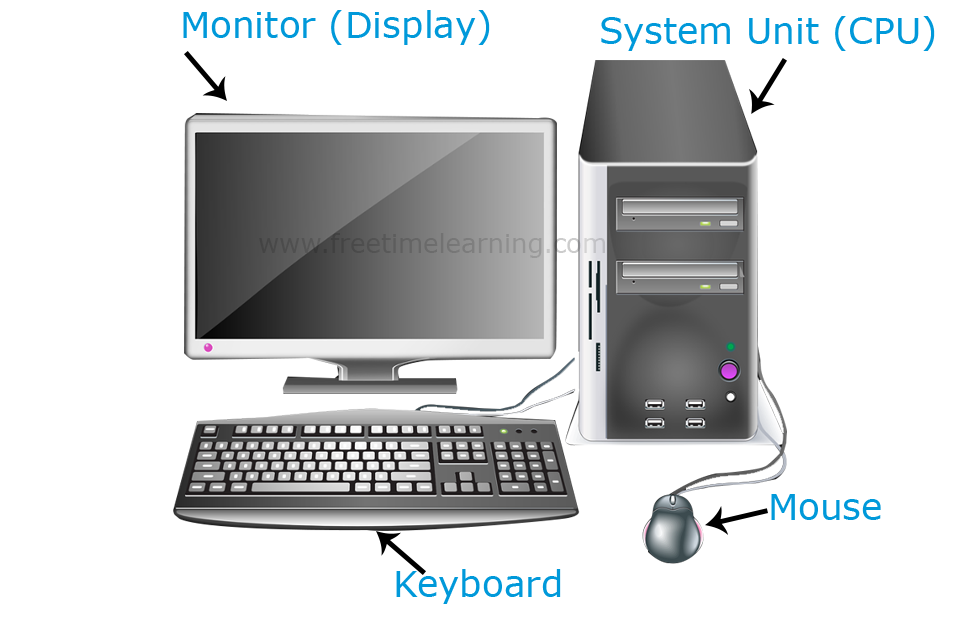
Input – Receiving data (e.g., from a keyboard, mouse, or sensor).
Processing – Performing calculations or logical operations (done by the CPU).
Storage – Saving data for immediate or future use (using RAM or hard drives).
Output – Displaying or transmitting the result (e.g., to a monitor or printer).
Control – Directing the manner and sequence of all operations.
Hardware: The physical parts (e.g., CPU, memory, motherboard, keyboard).
Software: Programs and operating systems that tell the hardware what to do.
Personal Computers (PCs) – For general use at home or office.
Laptops – Portable computers with built-in display and keyboard.
Servers – Powerful machines that provide data/services to other computers.
Supercomputers – Extremely fast computers used for complex calculations.
Embedded Systems – Computers built into other devices (e.g., washing machines, cars).
A computer is like a very fast and obedient assistant that follows exact instructions to solve problems, store information, and perform a wide range of tasks automatically.
Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML:
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented www |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2016 | W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1 |