| Basis of Comparison | Hub | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Hub is a networking device that connects the multiple devices to a single network. | A switch is a control unit that turns the flow of electricity on or off in a circuit. |
| Layer | Hubs are used at the physical layer. | Switches are used at the data link layer. |
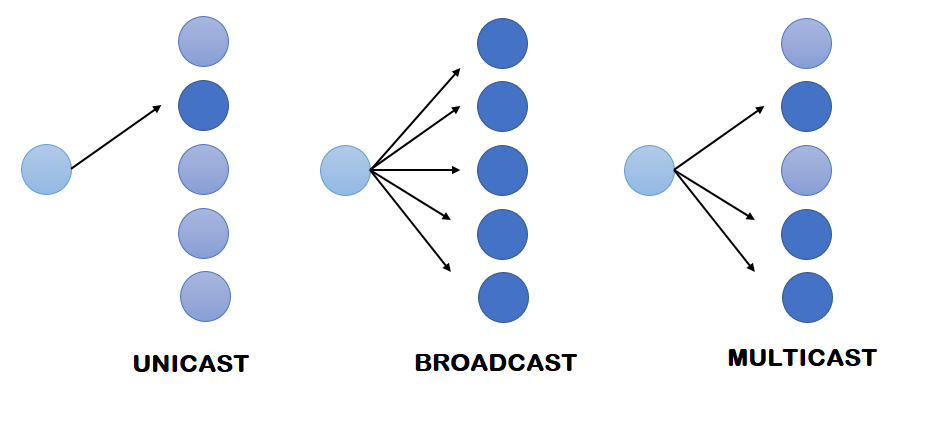
| Transmission type | Transmission type can be unicast, broadcast or multicast. | Initially, the transmission type is broadcast and then is unicast. |
| Ports | Hub has 4/12 ports. | The switch has 24/48 ports. |
| Transmission mode | Half duplex | Half/Full duplex. |
| Collisions | Collisions occur commonly in a Hub. | No collisions occur in a full duplex switch. |
| Address used for data transmission | Hub uses MAC address for data transmission. | The switch uses a MAC address for data transmission. |
| Data transmission form | Electrical signal is a data transmission form of a hub. | A Frame is a data transmission form of a switch. |
| Basis of Comparison | Router | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Description | It is a layer 3 device that connects the two different networks and identifies the network devices based on their IP addresses. | It is a layer 2 device and determines the network devices based on their MAC addresses. |
| Mode of transmission | Router transmits the data in the form of packets. | Switch transmits the data in the form of frames. |
| Address used | It uses an IP address for the data transmission. | It uses a MAC address to transmit the data. |
| Layer of OSI model | It uses Layer 3 OSI model and layer is the network layer. | It uses layer 2 OSI model and layer is the data link layer. |
| Table | It uses a routing table for routes to move to the destination IP. | It uses a Content address memory table for MAC addresses. |
| Network used | It is used for WAN and LAN networks. | It is used only for LAN networks. |
| Mode of transmission | Router is used in a full-duplex mode. | A switch is used in half as well as in a full-duplex mode. |
| User Mode | Privileged Mode |
|---|---|
| It is used for the regular task while using a Cisco router. | Offers a lot of options, including those available in User mode. |
| It enables you to view system information, connect to remote devices, check the status of the router, and more. | It allows users to make configurations on the router, such as making tests and debugging. |
| TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
|---|---|
| It is a connection-oriented protocol. | It is a connectionless protocol. |
| The connection should be established before the data is transmitted over the network. | It sends the data without checking whether the system is ready to receive it or not. |
| Delivery of data to the destination router is guaranteed. If the connection is lost during transferring files, the server would request the lost part. | It doesn’t guarantee the delivery of data to the destination. |
| The message will be delivered in the order it is sent. | The message may not be delivered in the same order. |
| It doesn’t support broadcasting. | It supports broadcasting. |
| Data is read as a stream. When one packet ends, another begins. | Data Packets are transmitted individually. |
| Header size is 20 bytes. | Header size is 8 bytes. |
| It is slower than UDP | UDP is faster and more efficient than TCP |
| This protocol is mainly used where a secure communication process is required. Example: web browsing and e-mail. | This protocol is used when fast communication is required. Example: VoIP, video, and music streaming. |
| Class | Range |
|---|---|
| A | 1-126 |
| B | 127-191 |
| C | 192-223 |
| D | 224-239 |
| E | 240-254 |
| Basis of Comparison | Static IP address | Dynamic IP address |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Static IP address is a fixed number assigned to the computer. | The dynamic IP address is a temporary number assigned to the computer. |
| Provided By | Static IP address is provided by ISP(Internet Service Provider). | The dynamic IP address is provided by DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). |
| Change requirement | It is static means that IP address does not change. | It is non-static means that IP address changes whenever the user connects to a network. |
| Security | It is not secure as IP address is constant. | It is secure because each time IP address changes. |
| Cost | It is costlier than Dynamic IP address. | It is cheaper than the Static IP address. |
| Device tracking | Static IP address is trackable as IP address is constant. | The dynamic IP address is untraceable as IP address is always changing. |
| CSMA/CD | CSMA/CA |
|---|---|
| Full form of CSMA/CD is carrier sense multiple access with collision detection. | Full form of CSMA/CA is carrier sense multiple access with carrier avoidance. |
| CSMA/CD detects the collision, and once the collision is detected, then it stops continuing the data transmission. | CSMA/CA does not deal with the recovery of the collision. |
| Wired installation is used in a CSMA/CD to detect the collision. | Wireless installation is used in a CSMA/CA as it avoids the collision. Therefore, it does not need a wired network. |
| An 802.3 Ethernet network uses CSMA/CD. | An 802.11 ethernet network uses CSMA/CA. |
| CSMA/CD takes effect after the occurrence of a collision. | CSMA/CA takes effect before the occurrence of a collision. |
| Public IP | Private IP |
|---|---|
| It is used on public networks. | It is mostly used within a private network or LAN to connect securely with other devices within the same network. |
| It is usually assigned by a Service provider or IANA. | It is usually assigned by a LAN administrator. |
| It is generally used to communicate outside the network. | It is generally used to communicate within the same network. |
| It can be known by searching “what is my IP” on google. | It can be known by typing “ipconfig” on the command prompt. |
| Its scope is global. | Its scope is local to the present network. |
| These come with a cost and are controlled by ISP. | These are free of cost and are used to load network OS. |
| It is routable and therefore, communication among different users is possible. | It is not routable and therefore, communication among different users is not possible. |
| It can be any number not included in the reserved private IP address range. Example: 202.60.23.1 |
Address ranges to be used by private networks are: Class A: 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 Class B: 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 Class C: 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 Example: 192.168.0.3 |
| Basis of Comparison | RIP | IGRP |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | RIP stands for routing information protocol. | IGRP stands for interior gateway routing protocol. |
| Description | RIP is a distance vector-based routing protocol. | IGRP is a distance vector based interior gateway routing protocol. |
| Determination of route | RIP depends on the number of hops to determine the best route to the network. | IGRP considers many factors before decides the best route to take, i.e., bandwidth, reliability, MTU and hops count. |
| Standard | RIP is a industry standard dynamic protocol. | IGRP is a Cisco standard dynamic protocol. |
| Organization used | RIP is mainly used for smaller sized organizations. | IGRP is mainly used for medium to large-sized organizations. |
| Maximum routers | It supports maximum 15 routers. | It supports a maximum 255 routers. |
| Symbol used | RIP is denoted by 'R' in the routing table. | IGRP is denoted by 'I' in the routing table. |
| Administrative distance | The administrative distance of RIP is 120. | The administrative distance of IGRP is 100. |
| Algorithm | RIP works on Bellman ford Algorithm. | IGRP works on Bellman ford Algorithm. |
Baud rate=bit rate / N,Sources : Cisco, and more..