Whenever an issue or defect is encountered while testing, it needs to be reported so that the developers can work on it and take the necessary action to fix it.
We will see step by step as how an issue is created in Atlassian JIRA.
1) Log in to your JIRA account by using valid credentials and get directed to the dashboard.
2) Click on ‘Create’ button displayed and you will be navigated to a window for creating an issue.
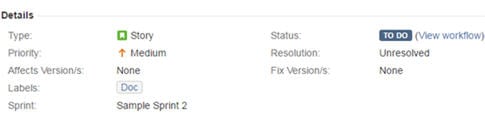
3) Enter all the necessary details as required to create an issue. The below field example can be understood better by the image below.
* In the Project field, a project for which we are creating an issue is selected. In this example: STH_Learning(STHL) is selected from the dropdown containing all the available projects.
* In the Issue type field, the nature of the issue is selected from the dropdown which contains options like Bug, Task, Improvement, Story, New Feature, etc. In this example, ‘Bug’ is the nature of the issue.
* The Summary field contains the one line title of the issue which imparts the critical information about the issue in a summarized way. The more effective the issue headline, the more you can show the criticality of the issue. Of course, the headline should be easily understood without any chances of misinterpretation. The example I have taken here, however, is not much critical.
* The Reporter is the one who reports the issue. In most of the cases, the name of the Project Manager is selected in this field.
* In Description field, the detailed description of the issue is written. As you can see in the below example screenshot, Steps to reproduce the issue, Actual result, Expected result are included in the description.
* In the Affect Version field, the current build version of the project is selected in which the issue has been encountered.
* Fix version field is basically selected by the concerned developer people, who choose the version as and when their work for the particular issue has been finished and the issue has been fixed.
* Priority field defines which issue should be considered first to be fixed. Tester selects the priority of the issue from the dropdown based on its effect on the application. This example issue is basically of a Medium priority.
* In the Attachment field, any video or screenshot related to the issue is being uploaded.
* In Environment field, operating system and browser details are mentioned on which issue has been encountered.
4) After all the details have been completed, click on the ‘Create’ button displayed on the window to create the new issue.
5) The issue id is generated which can be used in the future as a reference for tracking the progress of the issue.