composer requires laravel/passport{
"name": "laravel/laravel",
"type": "project",
"description": "The Laravel Framework.",
"keywords": [
"framework",
"laravel"
],
"license": "MIT",
"require": {
"php": "^7.3|^8.0",
"fideloper/proxy": "^4.4",
"fruitcake/laravel-cors": "^2.0",
"guzzlehttp/guzzle": "^7.0.1",
"laravel/framework": "^8.12",
"laravel/tinker": "^2.5"
},
"require-dev": {
"facade/ignition": "^2.5",
"fakerphp/faker": "^1.9.1",
"laravel/sail": "^1.0.1",
"mockery/mockery": "^1.4.2",
"nunomaduro/collision": "^5.0",
"phpunit/phpunit": "^9.3.3"
}
}composer.json specify production and dev packages and their version constraints respectively.php artisan make:migration<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration {
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::table('people', function (Blueprint $table)
{
$table->string('first_name')->nullable();
});
}
};
?><?php
return Model::query()
->whereNotExists(function($query) {
// $query is a Query\Builder
})
->whereHas('relation', function($query) {
// $query is an Eloquent\Builder
})
->with('relation', function($query) {
// $query is an Eloquent\Relation
});
?> Illuminate\Contracts\Database\QueryBuilder interface, as well as the Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Concerns\DecoratesQueryBuilder trait that will implement the interface in place of the __call magic method.str_contains(), str_starts_with(), and str_ends_with() internally in the \Illuminate\Support\Str class.HTTP middleware is a technique for filtering HTTP requests. Laravel includes a middleware that checks whether application user is authenticated or not.max()min()sum()avg()count() | Laravel Framework | CodeIgniter Framework |
|---|---|
| Relational object-oriented | Object-oriented |
| Supports custom HTTPS routes | Does not support HTTPS routes fully |
| Has authentication class features | No built-in authentication features |
| Has an inbuilt unit testing feature | No inbuilt unit testing feature |
| Use blade templates | Does not use blade templates |
| Not easy to learn for beginners | Easy to learn for beginners |
| Easy to develop REST APIs | Not easy to develop REST APIs |
| Supports ORM | Does not support ORM |
$validatedData = $request->validate([
'name' => 'required|max:255',
'username' => 'required|alpha_num',
'age' => 'required|numeric',
]);Route::get('login', 'users@login'); {{ HTML::link_to_action('users@login') }} composer create-project laravel/laravel --prefer-distphp artisan servephp artisan make:controller : Used for creating a Controller filephp artisan make:model : Used for making a Model filephp artisan make:migration : Used for making the Migration filephp artisan make:seeder : Used for making the Seeder filephp artisan make:factory : Used for making the Factory filephp artisan make:policy : Used for making the Policy filephp artisan make:command : Used for making a new artisan commandmake:middleware <middleware_name> command, helping define the new middleware within your application. By default, the middleware will get stored in the app/Http/Middleware directory. $middleware property of the app/Http/Kernel.php class. If you want to assign middleware specifically, assign it in the key-value pair at the app/Http/Kernel.php class $routeMiddleware property..blade.php.<!-- /resources/views/alert.blade.php -->
<div class="alert alert-danger">
{{ $slot }}
</div>$slot we can assign any value which we want to inject to component. Component looks like :@component('alert')
<strong>Whoops!</strong> Something went wrong!
@endcomponent
@component is the blade directive here.<form method="POST" action="/profile">
@csrf
...
</form>CSRF Protection middleware) can validate the request. VerifyCsrfToken middleware is included in web middleware group. @csrf blade directive can be used to generate the token field.resources/js/bootstrap.js is the default file which registers value of csrf-token meta tag with HTTP library.$except property where can provide URLs which we want to exclude.--table and --create options may be used to indicate the name of the table and whether the migration will be creating a new table. These options pre-fill the generated migration stub file with the specified table:make:migration create_employees_table --create=employeesmake:migration add_departments_to_employee_table --table=employees//Make authorization views and scaffolding
php artisan make:authRemove or comment out this line in app\Http\Kernel.php
\App\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken::class,app/Http/Middleware/VerifyCsrfToken.php" file and add your routes in $except array.namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken as BaseVerifier;
class VerifyCsrfToken extends BaseVerifier
{
/**
* The URIs that should be excluded from CSRF verification.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $except = [
'stripe/*',
'payment/verify/{id}/*',
'some/route/path',
];
Route::get($uri, $callback);Route::post($uri, $callback);Route::put($uri, $callback);Route::patch($uri, $callback);Route::delete($uri, $callback);Route::options($uri, $callback);php artisan downphp artisan upphp artisan make:seeder [className]<?php
use App\Models\Auth\User;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class UserTableSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Run the database seeds.
*/
public function run()
{
factory(User::class, 10)->create();
}
}run() method in the above code snippet will create 10 new users using the User factory.use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletes;
class Post extends Model {
use SoftDeletes;
protected $table = 'posts';
// ...
}php artisan make:model Postclass Post extends Model
{
/**
* The attributes that are mass assignable.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $fillable = [];
/**
* The attributes that should be hidden for arrays.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $hidden = [];
}
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class User extends Model
{
/**
* Get the addresses for the User.
*/
public function addresses()
{
return $this->hasMany(Address::class);
}
}
?>The above method phone on the User model can be called like : `$user->phone` or `$user->phone()->where(...)->get()`.
We can also define One to Many relationships like below :
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class User extends Model
{
/**
* Get the addresses for the User.
*/
public function addresses()
{
return $this->hasMany(Address::class);
}
}
?>
Since a user can have multiple addresses, we can define a One to Many relations between the User and Address model. Now if we call `$user->addresses`, eloquent will make the join between tables and it will return the result.
Route::middleware('auth:api', 'throttle:60,1')->group(function () {
Route::get('/user', function () {
//
});
});config/app.php configuration file that contains an array where you can mention the service provider class name. delete() : remove all record from the database table.softDeletes() : It does not remove the data from the table. It is used to flag any record as deleted.Insert() : This function is simply used to insert a record into the database. It not necessary that ID should be autoincremented.InsertGetId() : This function also inserts a record into the table, but it is used when the ID field is auto-increment.| Verb | Path | Action | Route Name | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /users | index | users.index | get all users |
| GET | /users/create | create | users.create | create a new user |
| POST | /users | store | users.store | store user details |
| GET | /users/{user} | show | users.show | get user details |
| GET | /users/{user}/edit | edit | users.edit | edit user |
| PUT/PATCH | /users/{user} | update | users.update | update user |
| DELETE | /users/{user} | destroy | users.destroy | delete user |
| GET Method | POST Method |
|---|---|
| Request data from a specific resource | Send data to a server |
| Parameters are included in the URL | Parameters are included in the body |
| Data is visible in the URL | Data is not visible in the URL |
| Only allowed characters are ASCII characters | Both ASCII characters and binary data are allowed |
| There is a limitation on data length | No limitation on data length |
| The request remains in the browser history | The request does not remain in the browser history |
| The request is possible to bookmark | The request is not possible to bookmark |
| Can be cached | Cannot be cached |
| Security is less compared to the POST method | Security is high compared to the GET method |
| Cannot be used to send sensitive data such as passwords | Can be used to send sensitive data such as passwords |
enableQueryLog method to enable query log in LaravelDB::connection()->enableQueryLog();
You can get array of the executed queries by using getQueryLog method:
$queries = DB::getQueryLog();php artisan cache: clearphp artisan config: clearphp artisan cache: clearphp artisan make: provider ClientsServiceProviderIlluminate\Support\ServiceProviderclass. Most of the service providers contain below-listed functions in its file :Register() FunctionBoot() FunctionRegister() method, one should only bind things into the service container. One should never attempt to register any event listeners, routes, or any other piece of functionality within the Register() method.whereBetween() method to retrieve the data between two dates with Query.Blog::whereBetween('created_at', [$date1, $date2])->get();use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
Route::get('/cache', function () {
return Cache::get('PutkeyNameHere');
})
IoC container.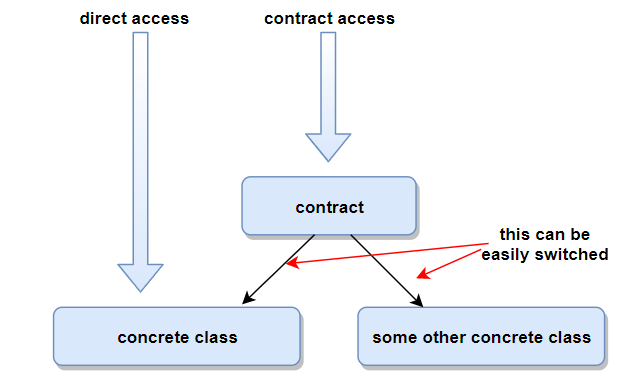
public function getUserIp(Request $request){
// Gettingip address of remote user
return $user_ip_address=$request->ip(); @yield for defining a section in a layout, getting the content from the child page, and submitting it to a master page. So whenever you use Laravel to execute the blade file, it first checks whether you have extended the master layout or not. If so, it moves to the master layout and commences getting the @sections. with() function is used to eager load. Rather than using two or more separate queries for fetching the data from a database, you can use the with() method after the first command. You will get a better user experience as you do not have to wait longer to fetch the data from the database. composer require laravel/tinkerphp artisan tinkerDB::table('blogs')->updateOrInsert([Conditions],[fields with value]);class User extends Model {
protected $guarded = ['role'];
// All fields inside the $guarded array are not mass-assignable
} protected $guarded = ['*']; $fillable serves as a "white list" whereas $guarded functions serves like a "black list". One should use either $fillable or $guarded.foreach (Product::where('name', 'bar')->cursor() as $flight) {
//make some stuff
}