while (expression1) :
statement_1
statement_2
......
if expression2 :
break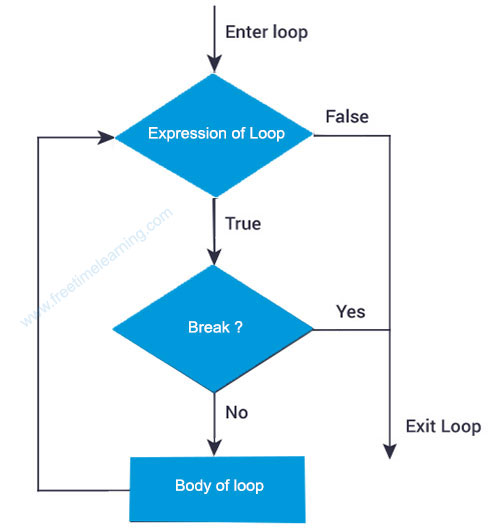
>>> for i in [1,2,3,4,5]:
if i==4:
print ("Element found")
break
print (i,)
1
2
3
Element found
>>> In the following example while loop breaks when the count value is 5. The print statement after the while loop displays the value of num_sum (i.e. 0+1+2+3+4).
>>> num_sum = 0
>>> count = 0
>>> while(count<10):
num_sum = num_sum + count
count = count + 1
if count== 5:
break
print("Sum of first ",count,"integers is : ", num_sum)
Sum of first 1 integers is : 0
Sum of first 2 integers is : 1
Sum of first 3 integers is : 3
Sum of first 4 integers is : 6
>>> The continue statement is used to skip the rest of the code inside a loop for the current iteration only. Loop does not terminate but continues on with the next iteration. The continue statement can be used in both while and for loops.
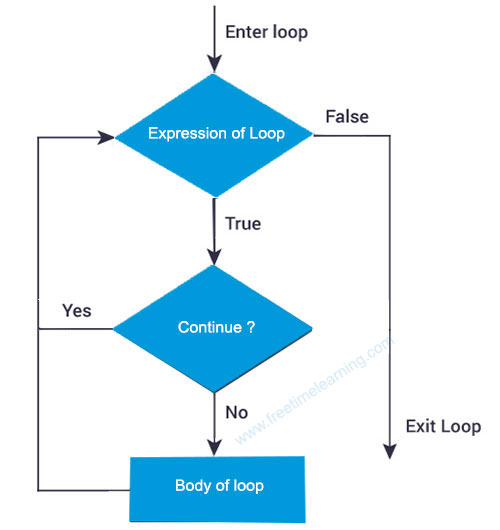
>>> a = 0
>>> while a<=5:
a=a+1
if a%2==0:
continue
print (a)
print ("End of Loop")
1
End of Loop
3
End of Loop
5
End of Loop
>>>