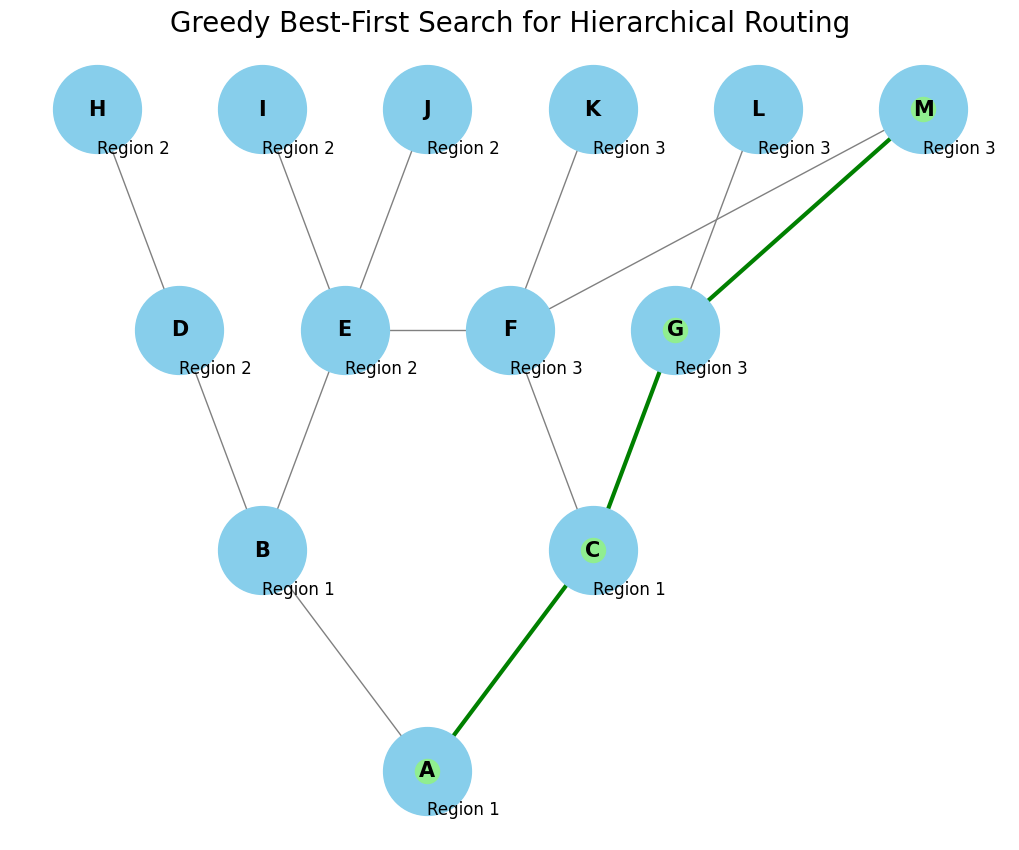
Greedy Best-First Search (GBFS) is a heuristic-based search algorithm used in artificial intelligence to find the most promising path from a start node to a goal node in a graph or tree. It prioritizes nodes that appear closest to the goal based on a heuristic function, making it efficient but not always optimal. Below is a detailed explanation:
# Node class to store information about each node
class Node:
def __init__(self, name, heuristic):
self.name = name
self.heuristic = heuristic
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.heuristic < other.heuristic# Greedy Best-First Search for Hierarchical Routing
def greedy_best_first_search_hierarchical(graph, start, goal, heuristic, region_map):
priority_queue = [] # Priority queue to hold nodes to explore, sorted by heuristic value
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(start, heuristic[start])) # Add start node
visited = set() # To keep track of visited nodes
path = {start: None} # Path dictionary to track explored paths
while priority_queue:
current_node = heapq.heappop(priority_queue).name # Get node with lowest heuristic
if current_node == goal: # Check if goal is reached
return reconstruct_path(path, start, goal)
visited.add(current_node) # Mark current node as visited
# Explore neighbors in the same region first
current_region = region_map[current_node]
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited and region_map[neighbor] == current_region:
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(neighbor, heuristic[neighbor]))
if neighbor not in path:
path[neighbor] = current_node
# Explore neighbors in other regions
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited and region_map[neighbor] != current_region:
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(neighbor, heuristic[neighbor]))
if neighbor not in path:
path[neighbor] = current_node
return None # If no path is found# Helper function to reconstruct the path from start to goal
def reconstruct_path(path, start, goal):
current = goal
result_path = []
while current is not None:
result_path.append(current) # Add node to path
current = path[current] # Move to the parent node
result_path.reverse() # Reverse the path to get the correct order
return result_path# Function to visualize the graph and the path
def visualize_graph(graph, path, pos, region_map):
G = nx.Graph()
# Add edges to the graph
for node, neighbors in graph.items():
for neighbor in neighbors:
G.add_edge(node, neighbor)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) # Set figure size
# Draw the nodes and edges
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, node_size=4000, node_color='skyblue',
font_size=15, font_weight='bold', edge_color='gray')
# Highlight the path
if path:
path_edges = list(zip(path, path[1:]))
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, edgelist=path_edges, edge_color='green', width=3)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, nodelist=path, node_color='lightgreen')
# Display region information on the graph
for node, region in region_map.items():
plt.text(pos[node][0], pos[node][1] - 0.2, f"Region {region}", fontsize=12, color='black')
plt.title("Greedy Best-First Search for Hierarchical Routing", size=20)
plt.show()# Complex graph with hierarchical regions
graph = {
'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['D', 'E'],
'C': ['F', 'G'],
'D': ['H'],
'E': ['I', 'J'],
'F': ['K' , 'M' , 'E'],
'G': ['L', 'M'],
'H': [], 'I': [], 'J': [], 'K': [], 'L': [], 'M': []
}
# Heuristic values (assumed for this example)
heuristic = {
'A': 8, 'B': 6, 'C': 7, 'D': 5, 'E': 4, 'F': 5, 'G': 4,
'H': 3, 'I': 2, 'J': 1, 'K': 3, 'L': 2, 'M': 1
}
# Define regions for the hierarchical routing (nodes belonging to different regions)
region_map = {
'A': 1, 'B': 1, 'C': 1, 'D': 2, 'E': 2, 'F': 3, 'G': 3,
'H': 2, 'I': 2, 'J': 2, 'K': 3, 'L': 3, 'M': 3
}# Define positions for better visualization layout (can be modified)
pos = {
'A': (0, 0), 'B': (-1, 1), 'C': (1, 1), 'D': (-1.5, 2),
'E': (-0.5, 2), 'F': (0.5, 2), 'G': (1.5, 2), 'H': (-2, 3),
'I': (-1, 3), 'J': (0, 3), 'K': (1, 3), 'L': (2, 3), 'M': (3, 3)
}
# Perform Greedy Best-First Search for hierarchical routing
start_node = 'A'
goal_node = 'M'
result_path = greedy_best_first_search_hierarchical(graph, start_node, goal_node, heuristic, region_map)
print("Path from {} to {}: {}".format(start_node, goal_node, result_path))
# Visualize the graph and the found path
visualize_graph(graph, result_path, pos, region_map)import heapq
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Node class to store information about each node
class Node:
def __init__(self, name, heuristic):
self.name = name
self.heuristic = heuristic
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.heuristic < other.heuristic
# Greedy Best-First Search for Hierarchical Routing
def greedy_best_first_search_hierarchical(graph, start, goal, heuristic, region_map):
# Priority queue to hold nodes to explore, sorted by heuristic value
priority_queue = []
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(start, heuristic[start]))
visited = set() # To keep track of visited nodes
# Path dictionary to track the explored paths
path = {start: None}
while priority_queue:
current_node = heapq.heappop(priority_queue).name
# If the goal is reached, reconstruct the path
if current_node == goal:
return reconstruct_path(path, start, goal)
visited.add(current_node)
# Explore neighbors in the same region first, then move to other regions
current_region = region_map[current_node]
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited and region_map[neighbor] == current_region:
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(neighbor, heuristic[neighbor]))
if neighbor not in path:
path[neighbor] = current_node
# Explore neighbors in other regions after same-region neighbors
for neighbor in graph[current_node]:
if neighbor not in visited and region_map[neighbor] != current_region:
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, Node(neighbor, heuristic[neighbor]))
if neighbor not in path:
path[neighbor] = current_node
return None # If no path is found
# Helper function to reconstruct the path from start to goal
def reconstruct_path(path, start, goal):
current = goal
result_path = []
while current is not None:
result_path.append(current)
current = path[current]
result_path.reverse()
return result_path
# Function to visualize the graph and the path
def visualize_graph(graph, path, pos, region_map):
G = nx.Graph()
# Add edges to the graph
for node, neighbors in graph.items():
for neighbor in neighbors:
G.add_edge(node, neighbor)
# Plot the graph
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
# Draw the nodes and edges
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, node_size=4000, node_color='skyblue', font_size=15, font_weight='bold', edge_color='gray')
# Highlight the path
if path:
path_edges = list(zip(path, path[1:]))
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, edgelist=path_edges, edge_color='green', width=3)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, nodelist=path, node_color='lightgreen')
# Display region information on the graph
for node, region in region_map.items():
plt.text(pos[node][0], pos[node][1] - 0.2, f"Region {region}", fontsize=12, color='black')
plt.title("Greedy Best-First Search for Hierarchical Routing", size=20)
plt.show()
# Complex graph with hierarchical regions
graph = {
'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['D', 'E'],
'C': ['F', 'G'],
'D': ['H'],
'E': ['I', 'J'],
'F': ['K' , 'M' , 'E'],
'G': ['L', 'M'],
'H': [],
'I': [],
'J': [],
'K': [],
'L': [],
'M': []
}
# Heuristic values (assumed for this example)
heuristic = {
'A': 8,
'B': 6,
'C': 7,
'D': 5,
'E': 4,
'F': 5,
'G': 4,
'H': 3,
'I': 2,
'J': 1,
'K': 3,
'L': 2,
'M': 1
}
# Define regions for the hierarchical routing (nodes belonging to different regions)
region_map = {
'A': 1, 'B': 1, 'C': 1,
'D': 2, 'E': 2,
'F': 3, 'G': 3,
'H': 2, 'I': 2, 'J': 2,
'K': 3, 'L': 3, 'M': 3
}
# Define positions for better visualization layout (can be modified)
pos = {
'A': (0, 0),
'B': (-1, 1),
'C': (1, 1),
'D': (-1.5, 2),
'E': (-0.5, 2),
'F': (0.5, 2),
'G': (1.5, 2),
'H': (-2, 3),
'I': (-1, 3),
'J': (0, 3),
'K': (1, 3),
'L': (2, 3),
'M': (3, 3)
}
# Perform Greedy Best-First Search for hierarchical routing
start_node = 'A'
goal_node = 'M'
result_path = greedy_best_first_search_hierarchical(graph, start_node, goal_node, heuristic, region_map)
print("Path from {} to {}: {}".format(start_node, goal_node, result_path))
# Visualize the graph and the found path
visualize_graph(graph, result_path, pos, region_map)Path from A to M: ['A', 'C', 'G', 'M']