
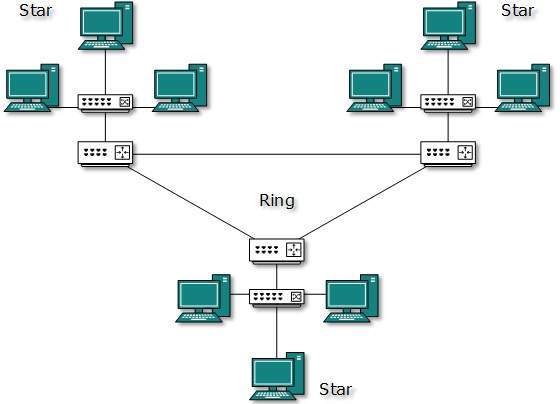
| IPv4 Class | Private IPv4 Start Address | Private IPv4 End Address |
|---|---|---|
| A | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 |
| B | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 |
| B | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 |
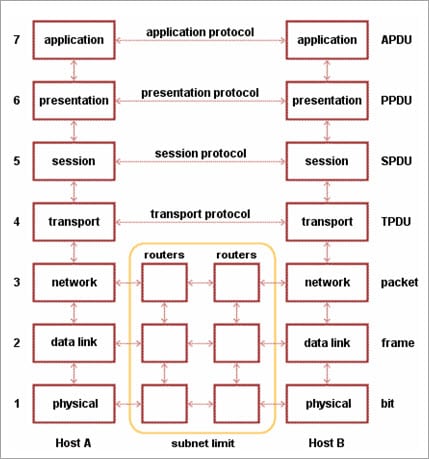
| Layer | Unit Exchanged | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Bit |
|
| Data Link | Frame |
|
| Network | Packet |
|
| Transport | TPDU - Transaction Protocol Data Unit |
|
| Session | SPDU - Session Protocol Data Unit |
|
| Presentation | PPDU - Presentation Protocol Data Unit |
|
| Application | APDU - Application Protocol Data Unit |
|
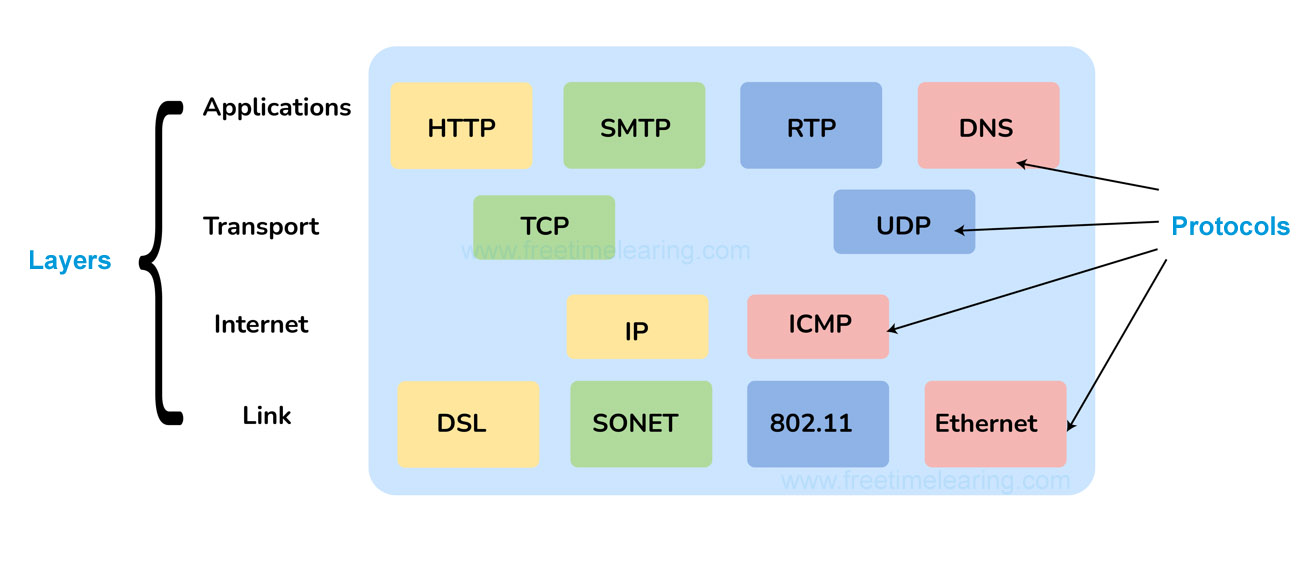
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Link | Decides which links such as serial lines or classic Ethernet must be used to meet the needs of the connectionless internet layer. |
| Internet |
|
| Transport | Its functionality is almost the same as the OSI transport layer. It enables peer entities on the network to carry on a conversation. |
| Application | It contains all the higher-level protocols. |
| TCP/IP | UDP |
|---|---|
| Connection-Oriented Protocol | Connectionless Protocol |
| More Reliable | Less Reliable |
| Slower Transmission | Faster Transmission |
| Packets order can be preserved or can be rearranged | Packets order is not fixed and packets are independent of each other |
| Uses three ways handshake model for connection | No handshake for establishing the connection |
| TCP packets are heavy-weight | UDP packets are light-weight |
| Offers error checking mechanism | No error checking mechanism |
| Protocols like HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SMTP, HTTPS, etc use TCP at the transport layer | Protocols like DNS, RIP, SNMP, RTP, BOOTP, TFTP, NIP, etc use UDP at the transport layer |
| Hub | Switch |
|---|---|
| A hub operates on the physical layer. | A switch operates on the data link layer. |
| Hubs perform frame flooding that can be unicast, multicast, or broadcast. | It performs broadcast, then the unicast and multicast as needed. |
| Just a singular domain of collision is present in a hub. | Varied ports have separate collision domains. |
| The transmission mode is Half-duplex | The transmission mode is Full duplex |
| Hubs operate as a Layer 1 device per the OSI model. | Network switches help you to operate at Layer 2 of the OSI model. |
| To connect a network of personal computers should be joined through a central hub. | Allow connecting multiple devices and ports. |
| Uses electrical signal orbits | Uses frame & packet |
| Does not offer Spanning-Tree | Multiple Spanning-Tree is possible |
| Collisions occur mostly in setups using hubs. | No collisions occur in a full-duplex switch. |
| Hub is a passive device | A switch is an active device |
| A network hub can’t store MAC addresses. | Switches use CAM (Content Accessible Memory) that can be accessed by ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Chips). |
| Not an intelligent device | Intelligent device |
| Its speed is up to 10 Mbps | 10/100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps |
| Does not use software | Has software for administration |
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 has a 32-bit address length | IPv6 has a 128-bit address length |
| It Supports Manual and DHCP address configuration | It supports Auto and renumbering address configuration |
| In IPv4 end to end, connection integrity is Unachievable | In IPv6 end to end, connection integrity is Achievable |
| It can generate 4.29×109 address space | Address space of IPv6 is quite large it can produce 3.4×1038 address space |
| The Security feature is dependent on application | IPSEC is an inbuilt security feature in the IPv6 protocol |
| Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal | Address Representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal |
| Fragmentation performed by Sender and forwarding routers | In IPv6 fragmentation performed only by the sender |
| In IPv4 Packet flow identification is not available | In IPv6 packet flow identification are Available and uses the flow label field in the header |
| In IPv4 checksum field is available | In IPv6 checksum field is not available |
| It has broadcast Message Transmission Scheme | In IPv6 multicast and anycast message transmission scheme is available |
| In IPv4 Encryption and Authentication facility not provided | In IPv6 Encryption and Authentication are provided |
| IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. | IPv6 has header of 40 bytes fixed |
:’. | ipconfig | ifconfig |
|---|---|
| Internet Protocol Configuration | Interface Configuration |
| Command used in Microsoft operating systems to view and configure network interfaces | Command used in MAC, Linux, UNIX operating systems to view and configure network interfaces |
|
Used to get the TCP/IP summary and allows to changes the DHCP and DNS settings |
|
| Forward DNS lookup | Reverse DNS lookup |
|---|---|
| Converts a human input or a domain name to an IP address | Converts an IP address into a domain name |
| Has a mapping between hostnames and IP addresses | Has a mapping that relates IP addresses to hostnames |
| Used for a website or other server access | Used for network troubleshooting |
| Utilizes different servers with different IP addresses | Resolves reverse lookup queries where a client requests a hostname by providing an IP address |
| Uses A Records (basic) to identify any IP address for a particular hostname | Uses DNS pointer record to identify a hostname for a given IP address |
10-bit Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) for unique channel addressing. There are two types of connections :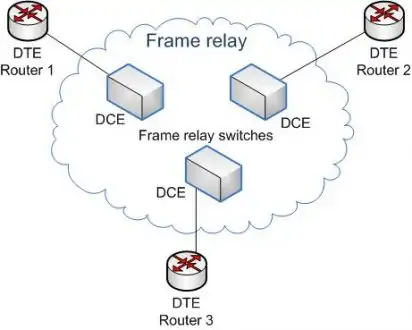
Start” button on your computercdm”Enter”nslookup freetimelearning.com”. Instead of “freetimelearning.com”, you must write the domain name of the page you want to consult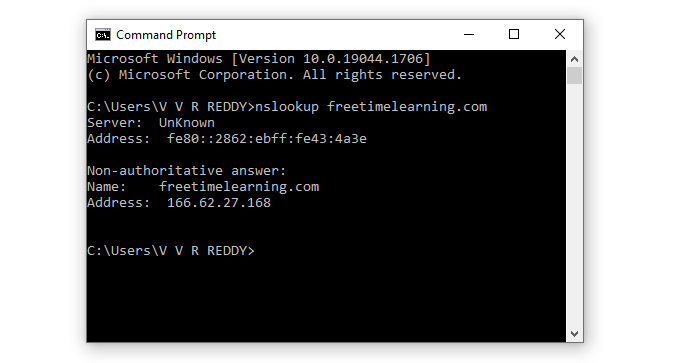
| Workgroup | Domain |
|---|---|
| All computers are peers and no computer has control over another computer | Network admin uses one or more computer as a server and provide all accesses, security permission to all other computers in a network |
| In a Workgroup, each computer maintains their own database | The domain is a form of a computer network in which computers, printers, and user accounts are registered in a central database. |
| Each computer has their own authentication rule for every user account | It has centralized authentication servers which set the rule of authentication |
| Each computer has set of user account. If user has account on that computer then only user able to access the computer | If user has an account in a domain then user can login to any computer in a domain |
| Workgroup does not bind to any security permission or does not require any password | Domain user has to provide security credentials whenever they are accessing the domain network |
| Computer settings need to change manually for each computer in a Workgroup | In a domain, changes made in one computer automatically made same changes to all other computers in a network |
| All computers must be on same local area network | In a domain, computers can be on a different local network |
| In a Workgroup, there can be only 20 computers connected | In a domain, thousands of computers can be connected |
IEEE 802.1D. STP runs on 802.1D-compliant bridges and switches to prevent loops in a network. The configuration of STP requires a well-planned network topology by the administrator. STP increases the reliability of the network exponentially by introducing redundancy that is as important as backups in case an active link within the network fails. port 21, and it is supported by the majority of web browsers.explicit,” making the acronym stand for File Transfer Protocol over explicit transport layer security (TLS)/SSL. This type of FTP begins like regular FTP, using port 21, but then special commands upgrade it to a TLS/SSL-encrypted transmission. Because it tends to work well with firewalls, some prefer to use FTPES over FTPS.| S.NO | Bluetooth | Wifi |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bluetooth has no full form. | While wifi stands for Wireless Fidelity. |
| 2. | It requires bluetooth adapter on all devices for connectivity. | Whereas it requires a wireless adapter Bluetooth for all devices and a wireless router for connectivity. |
| 3. | Bluetooth consumes low power. | while it consumes high power. |
| 4. | The security of BlueTooth is less in comparison to the number of wifi. | While it provides better security than BlueTooth. |
| 5. | Bluetooth is less flexible means these limited users are supported. | Whereas wifi supports large amount of users. |
| 6. | The radio signal range of BlueTooth is ten meters. | Whereas in wifi this range is a hundred meters. |
| 7. | Bluetooth requires low bandwidth. | While it requires high bandwidth. |
| MAC | IP address |
|---|---|
| The MAC address stands for Media Access Control Address. | IP address stands for Internet Protocol Address. |
| It consists of a 48-bit address. | It consists of a 32-bit address. |
| MAC address works at the link layer of the OSI model. | IP address works at the network layer of OSI model. |
| It is referred to as a physical address. | It is referred to as a logical address. |
| You can retrieve the MAC address of any device using ARP protocol. | You can retrieve the MAC address of any device RARP protocol. |
| Classes are not used in MAC address. | In IP, IPv4 uses A, B, C, D, and E classes. |