Correct Answer : 5.5x 10-7 A
Explaination : I=I0×(e(V/ηVT) – 1) where I0 = reverse saturation current
η = ideality factor
VT = thermal voltage
V = applied voltage
Here, I = 0.1mA, η = 1.5, V = 0.2V, VT = TK/11600
Therefore, VT at T = 25+273=298 is 298/11600 = 0.0256V.
Therefore, reverse saturation current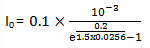
IO=0.00055mA = 5.5×10-7A.