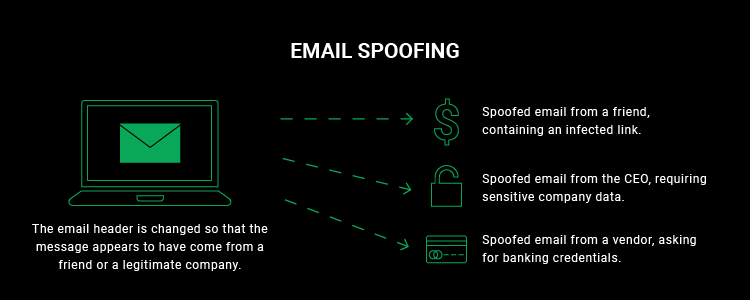
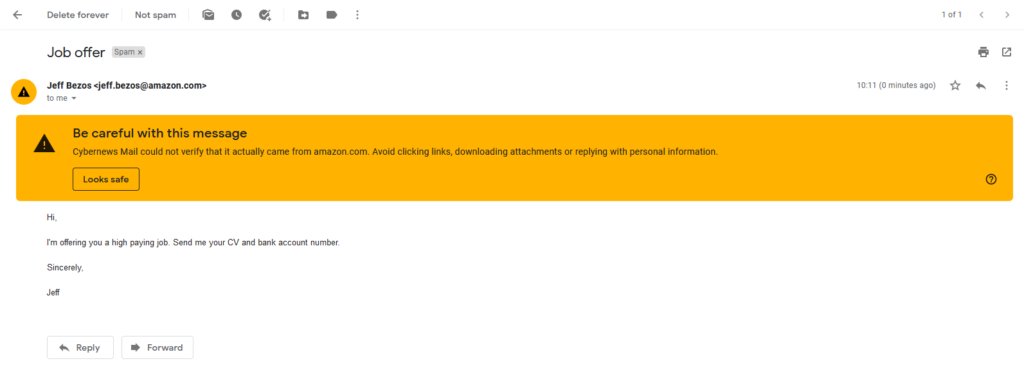
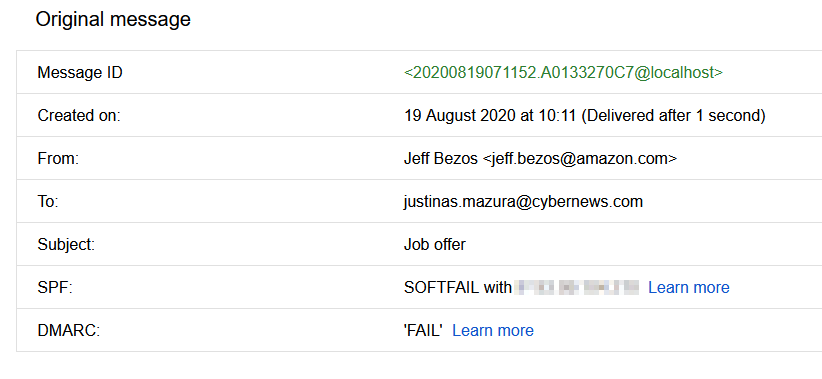
SQL Injection types exist in different categories; however, they are all concerned with an attacker introducing random SQL into a web page or web application database query. The easiest method of SQL Injection is via user input. Typically, web apps receive user input using a form. So, the front end sends the user input to the back-end database for processing.
In the situation when the web application fails to sanitize user input, the attacker can introduce the SQL they select into the back-end database and duplicate, modify, or remove the contents of the database. SQL Injection types can be categorized into three main groupings, including In-band SQLi, Out-of-band SQLi, and Blind or Inferential SQLi.
* In-band SQLi : In-band SQL Injection happens when an unscrupulous hacker can effectively apply the same communication channel for introducing an attack and collating the results. Attackers exploit the same channel of communication to introduce their attacks and to assemble their outcomes. In-band SQL Injection is one of the simplest and most popular SQL Injection attacks, making it easy to exploit. The two popularly known sub-categories of in-band SQL Injection include.
* Error-based SQLi : This is an in-band SQL Injection practice where an attacker executes actions that lead to error messages. These error messages are cast by the database server to gain data regarding the structure of the database. Although errors are extremely valuable during the development stage of a web application, these should be logged to a file with limited access or deactivated on a live site.
* Union-based SQLi : Union-based SQL Injection technique takes advantage of the UNION SQL operator to merge the results of multiple SELECT statements to get a single result that is afterward sent back as part of the HTTP response. This attacker leverages the data from this response.
* Out-of-band SQLi : Unlike the in-band SQLi technique, the out-of-band SQLi technique is not as popular. The reason is that an attacker can only perform this type of attack when specified features are activated on the database server engaged by the web page. This type of attack is mostly used when an attacker is unable to use the same channel to introduce the attack and assemble results.
It is an alternative to the Blind and in-band SQLi practices, particularly when the server responses are less steady. Out-of-band SQLi procedures matter based on the capability of the server to generate HTTP or DNS requests to transmit data back to an attacker
* Blind or Inferential SQLi : Most situations of an SQL Injection attack are blind vulnerabilities. This is because applications do not send back SQL query results or the particulars of database errors within its responses. As an alternative, an attacker who can reconstruct the structure of the database by transmitting payloads monitors the response of the web application and the ensuing performances of the database server. This is often more complicated and difficult for an attacker to exploit, but it is as dangerous as any other form of SQL Injection available. Inferential or blind SQLi can be grouped into two sub–categories.
* Time-Based : Using this blind technique, the attacker transfers a SQL query to the database, making the database hold for some seconds before responding. Time-based SQLi depends on transferring an SQL query to the database, which in turn influences the database to halt for a short period, usually in seconds, before it can react. The attacker can observe from the response time whether the ensuing query is true or false.
Depending on the result, an HTTP response is created immediately or after a delay. The attacker can, therefore, understand if the message they applied returned true or false, without depending on the data from the database. This type of attack is often time-consuming, particularly when large databases are involved because a requirement for an attacker is that they should itemize the database character by character. 
* Boolean or Content-based : This blind SQLi technique is used by an attacker to send a SQL query to the database, forcing the application to generate a result. Depending on whether the query is true or false, varying results would be generated. Also, depending on the returned result, the content within the HTTP response is altered or remains unaffected. Afterward, the attacker can determine whether the message created is a true or false result.
Source : Eccouncil