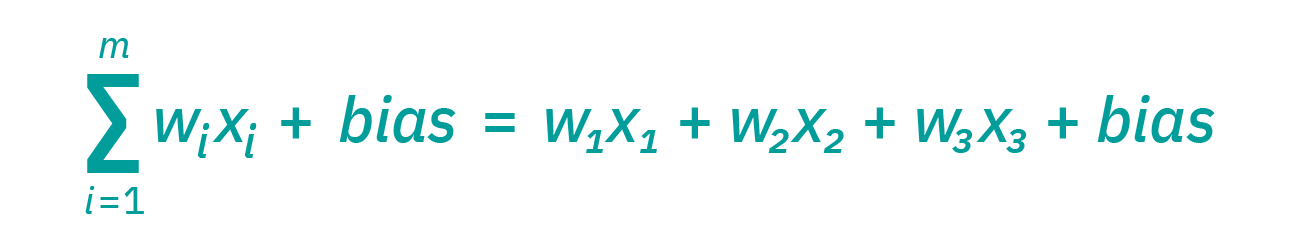
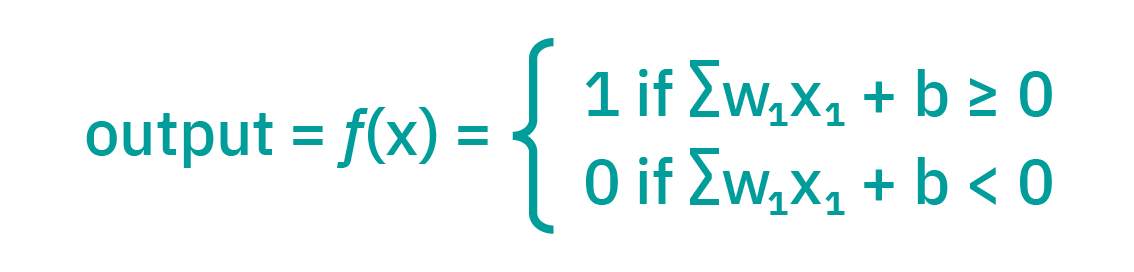
| DIFFERENCE BETWEEN | NEURAL NETWORKS | DEEP LEARNING SYSTEMS |
|---|---|---|
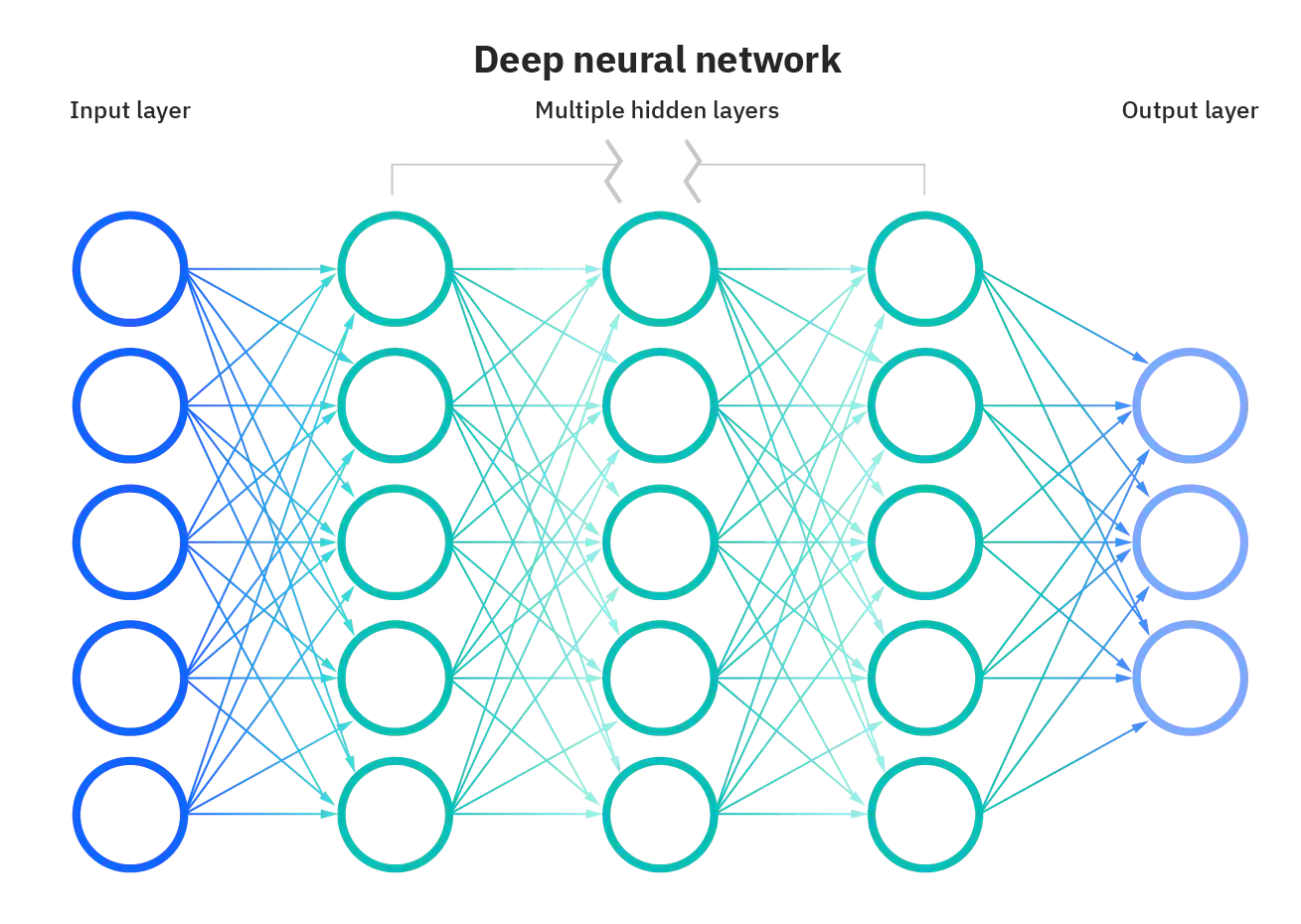
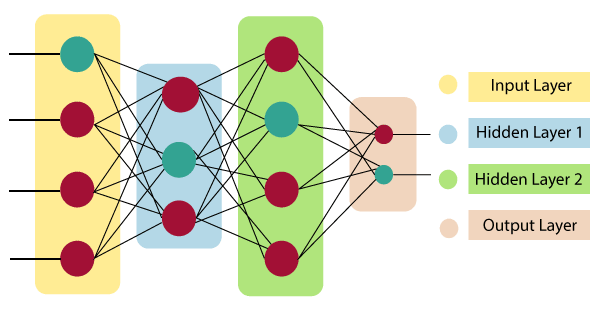
| Definition | A neural network is a model of neurons inspired by the human brain. It is made up of many neurons that at inter-connected with each other. | Deep learning neural networks are distinguished from neural networks on the basis of their depth or number of hidden layers. |
| Architecture |
Feed Forward Neural Networks Recurrent Neural Networks Symmetrically Connected Neural Networks |
Recursive Neural Networks Unsupervised Pre-trained Networks Convolutional Neural Networks |
| Structure |
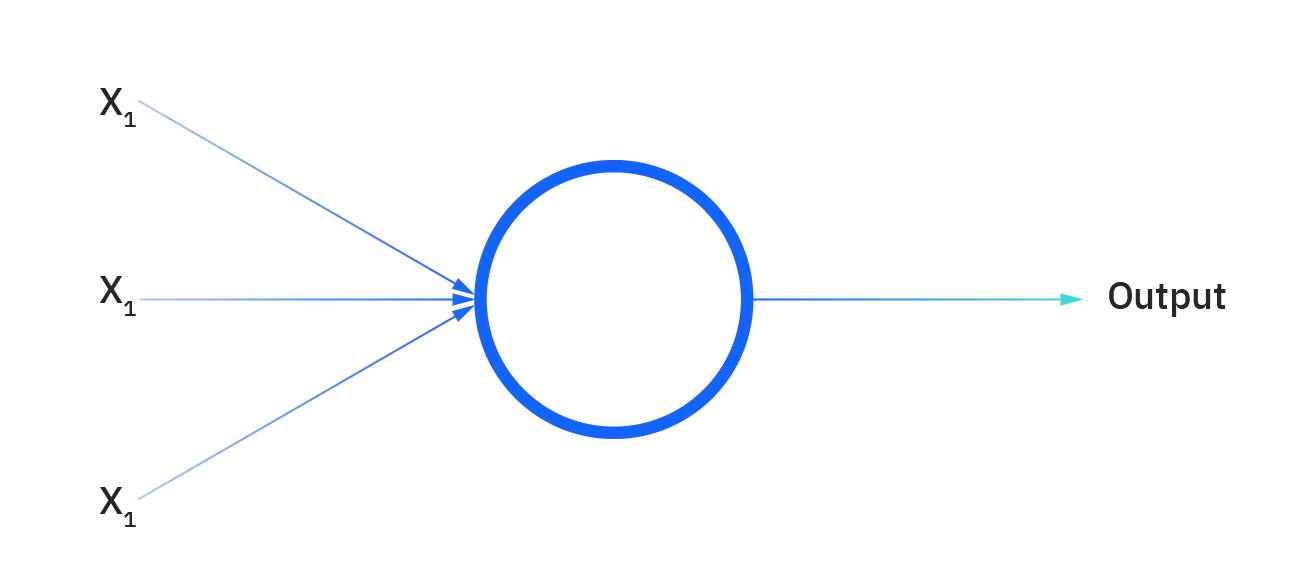
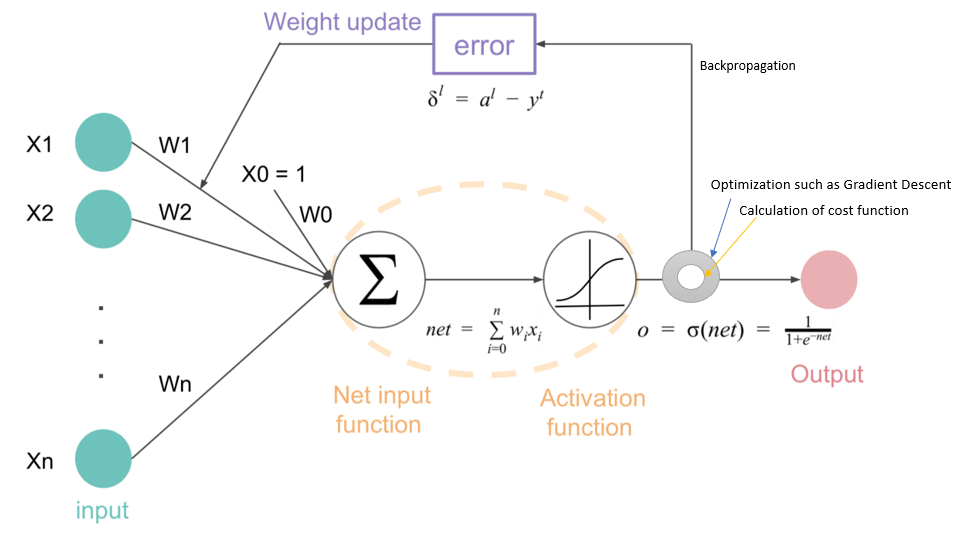
Neurons Connection and weights Propagation function Learning rate |
Motherboards PSU RAM Processors |
| Time & Accuracy |
It generally takes less time to train them. They have a lower accuracy than Deep Learning Systems |
It generally takes more time to train them. They have a higher accuracy than Deep Learning Systems |
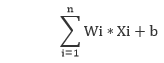
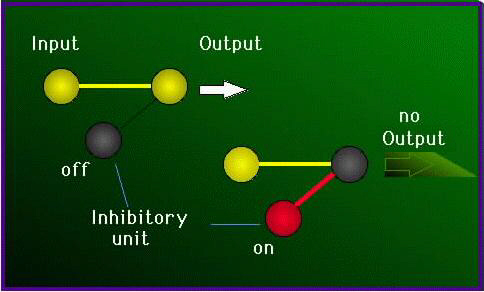
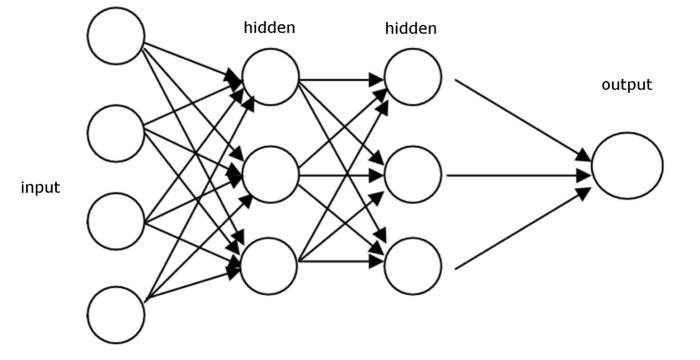
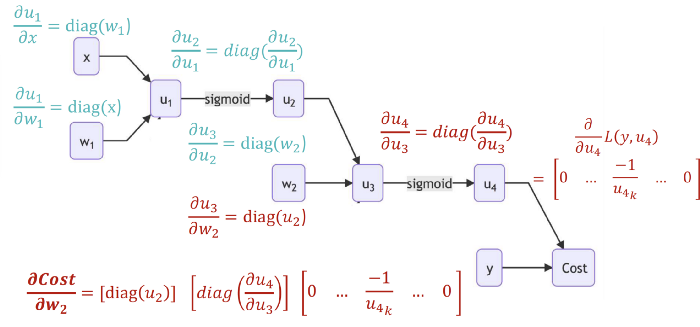
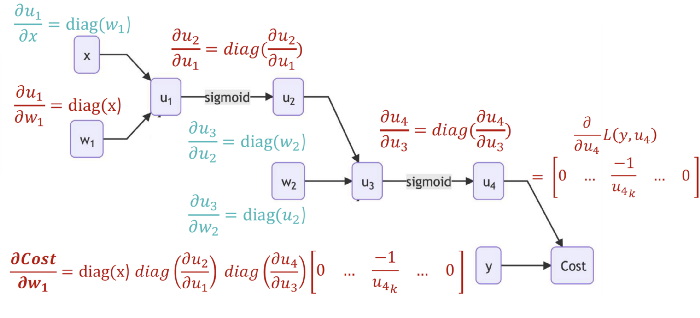
| Biological Neurons | Artificial Neurons |
|---|---|
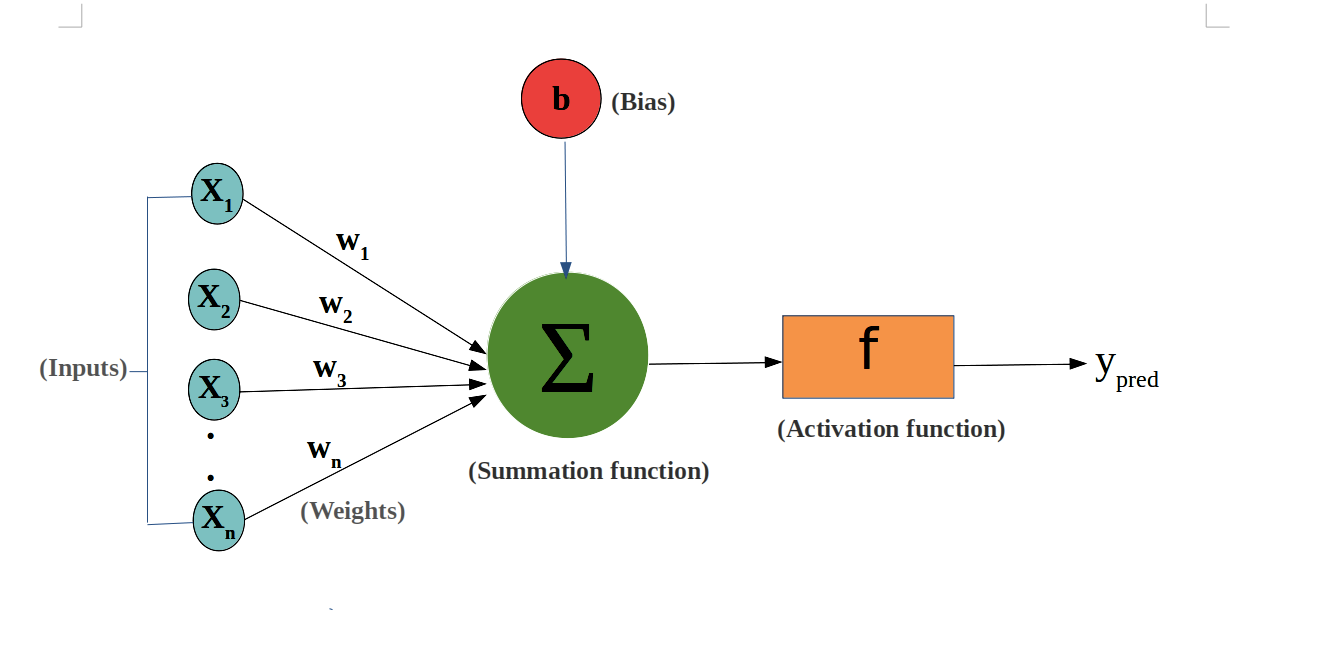
| Major components: Axions, Dendrites, Synapse | Major Components: Nodes, Inputs, Outputs, Weights, Bias |
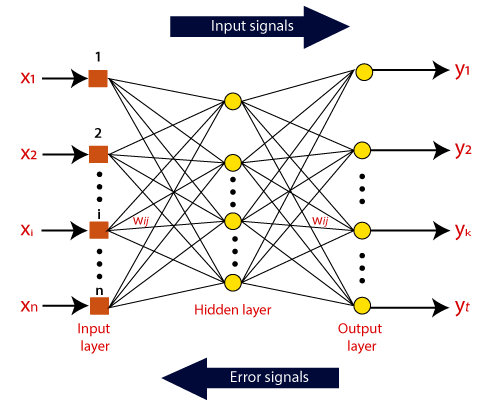
| Information from other neurons, in the form of electrical impulses, enters the dendrites at connection points called synapses. The information flows from the dendrites to the cell where it is processed. The output signal, a train of impulses, is then sent down the axon to the synapse of other neurons. | The arrangements and connections of the neurons made up the network and have three layers. The first layer is called the input layer and is the only layer exposed to external signals. The input layer transmits signals to the neurons in the next layer, which is called a hidden layer. The hidden layer extracts relevant features or patterns from the received signals. Those features or patterns that are considered important are then directed to the output layer, which is the final layer of the network. |
| A synapse is able to increase or decrease the strength of the connection. This is where information is stored. | The artificial signals can be changed by weights in a manner similar to the physical changes that occur in the synapses. |
| Approx 1011 neurons. | 102– 104 neurons with current technology |
| Human Brain(Biological Neuron Network) | Computers(Artificial Neuron Network) |
|---|---|
| The human brain works asynchronously | Computers(ANN) work synchronously. |
| Biological Neurons compute slowly (several ms per computation) | Artificial Neurons compute fast (<1 nanosecond per computation) |
| The brain represents information in a distributed way because neurons are unreliable and could die any time. | In computer programs every bit has to function as intended otherwise these programs would crash. |
| Our brain changes their connectivity over time to represents new information and requirements imposed on us. | The connectivity between the electronic components in a computer never change unless we replace its components. |
| Biological neural networks have complicated topologies. | ANNs are often in a tree structure. |
| Researchers are still to find out how the brain actually learns. | ANNs use Gradient Descent for learning. |
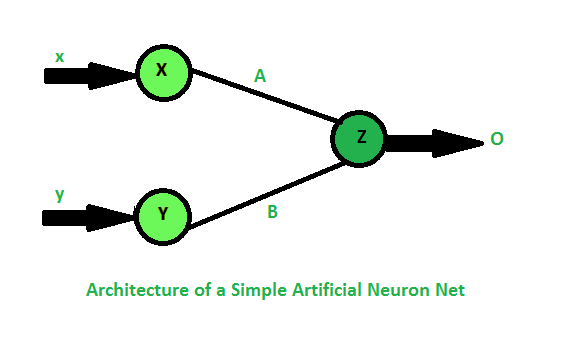
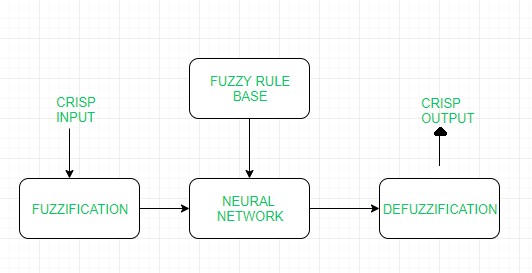
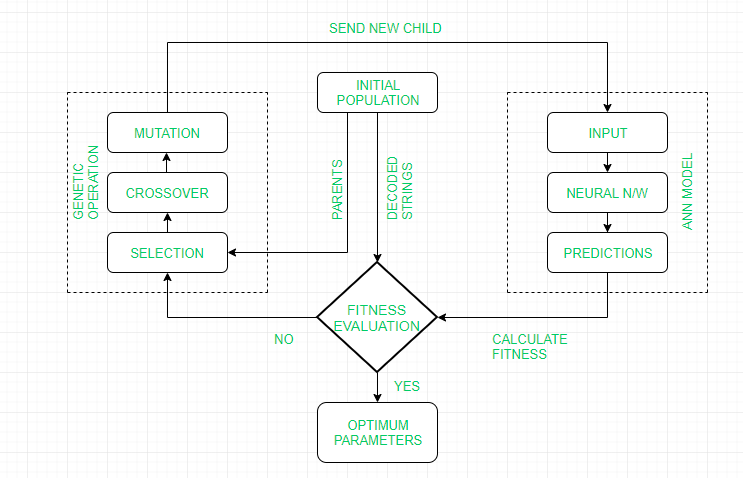
| S.NO | Soft Computing | Hard Computing |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soft Computing is liberal of inexactness, uncertainty, partial truth and approximation. | Hard computing needs a exactly state analytic model. |
| 2. | Soft Computing relies on formal logic and probabilistic reasoning. | Hard computing relies on binary logic and crisp system. |
| 3. | Soft computing has the features of approximation and dispositionality. | Hard computing has the features of exactitude(precision) and categoricity. |
| 4. | Soft computing is stochastic in nature. | Hard computing is deterministic in nature. |
| 5. | Soft computing works on ambiguous and noisy data. | Hard computing works on exact data. |
| 6. | Soft computing can perform parallel computations. | Hard computing performs sequential computations. |
| 7. | Soft computing produces approximate results. | Hard computing produces precise results. |
| 8. | Soft computing will emerge its own programs. | Hard computing requires programs to be written. |
| 9. | Soft computing incorporates randomness . | Hard computing is settled. |
| 10. | Soft computing will use multivalued logic. | Hard computing uses two-valued logic. |
| S.NO. | A.I. | SOFT COMPUTING |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Artificial Intelligence is the art and science of developing intelligent machines. | Soft Computing aims to exploit tolerance for uncertainty, imprecision, and partial truth. |
| 2 | AI plays a fundamental role in finding missing pieces between the interesting real world problems. | Soft Computing comprises techniques which are inspired by human reasoning and have the potential in handling imprecision, uncertainty and partial truth. |
| 3 | Branches of AI :
1. Reasoning 2. Perception 3. Natural language processing |
Branches of soft computing :
1. Fuzzy systems 2. Evolutionary computation 3. Artificial neural computing |
| 4 | AI has countless applications in healthcare and widely used in analyzing complicated medical data. | They are used in science and engineering disciplines such as data mining, electronics, automotive, etc. |
| 5 | Goal is to stimulate human-level intelligence in machines. | It aims at accommodation with the pervasive imprecision of the real world. |
| 6 | They require programs to be written. | They not require all programs to be written, they can evolve its own programs. |
| 7 | They require exact input sample. | They can deal with ambiguous and noisy data. |