A is used for encryption, we have to use the private key of the same user for decryption.p and q where p not equal to q.Calculate n= p*q and z=(p-1)*(q-1)ed-1) is exactly divisible by 2.n, d, and ec=m pow(e) mod n(where m is plain text and c is ciphertext)m= c pow(d) mod ne, n) is the public key used for encryption. (d, n) is the private key used for decryption| IDS | IPS |
|---|---|
| IDS stands for Intrusion Detection Systems. | IPS stands for Intrusion Prevention Systems. |
| IDS can only detect intrusions, but it is unable to prevent intrusions. | IPS can detect as well as prevent intrusions. |
| IDS is a monitoring system. | IPS is a control system. |
| IDS requires a human or another system to look at the results. | IPS only requires a regularly updated database with the latest threat data. |
Risk = likelihood of a threat * Vulnerability Impact| Basis of Comparison | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption key | Same key for encryption & decryption | Different keys for encryption & decryption |
| Performance | Encryption is fast but more vulnerable | Encryption is slow due to high computation |
| Algorithms | DES, 3DES, AES and RC4 | Diffie-Hellman, RSA |
| Purpose | Used for bulk data transmission | Often used for securely exchanging secret keys |
traditional” firewall, a stateful inspection firewall allows or blocks traffic based on state, port, and protocol. It monitors all activity from the opening of a connection until it is closed. Filtering decisions are made based on both administrator-defined rules as well as context, which refers to using information from previous connections and packets belonging to the same connection.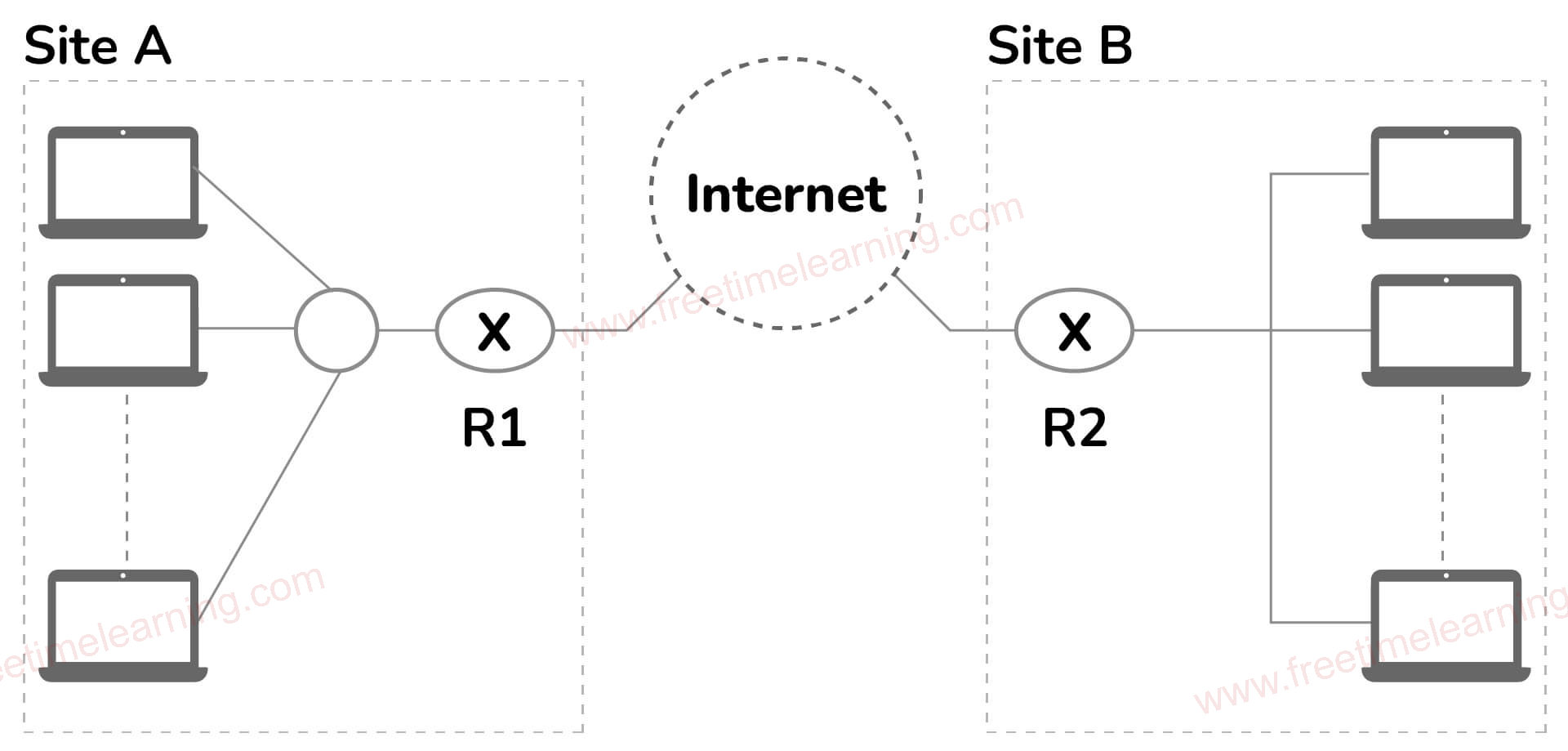

| Hashing | Encryption |
|---|---|
| It is a method of converting data to a smaller fixed value known as the key, which is then used to represent the original data. | It's the technique of securely encoding data such that only the authorized user with the key or password can get the original data; for everyone else, it seems to be rubbish. |
| By whatever method, the hash code or key cannot be reverted to the original information. It can only be mapped, and the hash code is compared; if the hash code is the same, the information is identical; otherwise, it is not. It is not possible to get the original data. | If we know the encryption key and technique used for encryption, we can easily extract the original data. |
| In comparison to encryption, it is more secure. | In comparison to hashing, it is less secure. |
| The goal of hashing is to index and retrieve data from a database. The procedure is really quick. | Encryption transforms data in order to keep it hidden from others. |
| The hashed data is usually short and constant in length. It does not increase in size as the length of information increases. | The length of the encrypted data is not defined. It expands as the amount of data grows longer. |
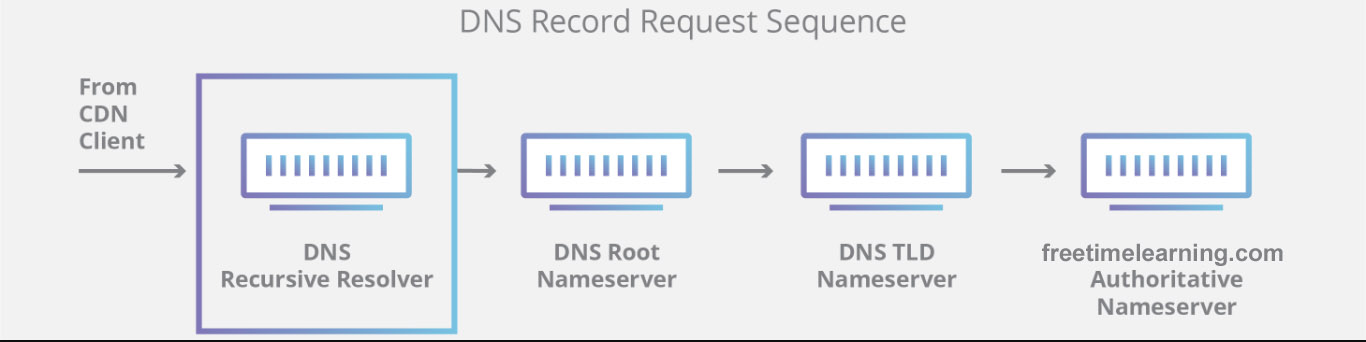
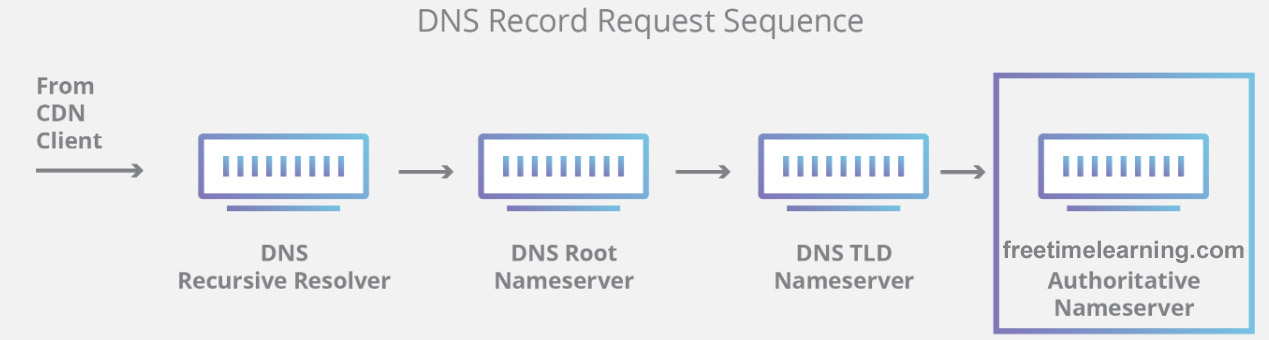
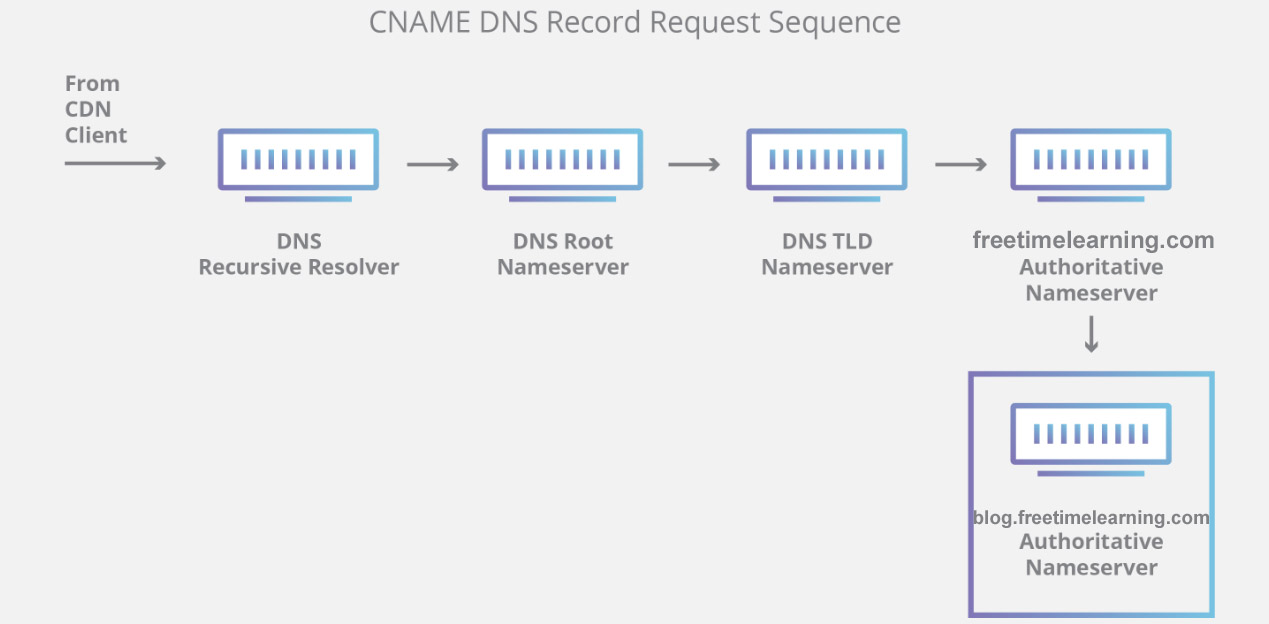
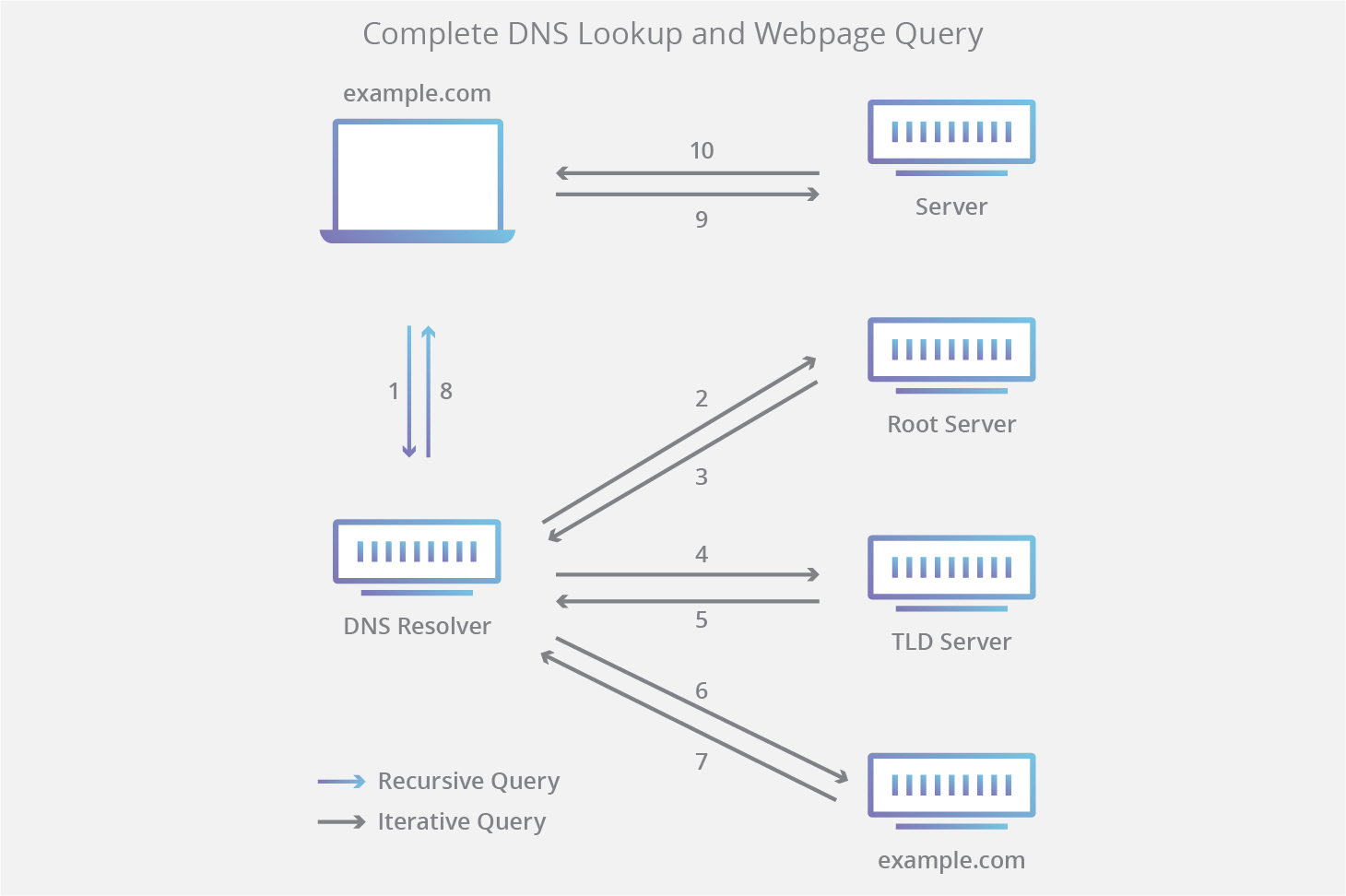

| Vulnerability Assessment (VA) | Penetration Testing (PT) |
| Identifies the vulnerabilities in a network | Identifies vulnerabilities to exploit them to penetrate the system |
| Tells how susceptible the network is | Tells whether the detected vulnerability is genuine |
| Conducted at regular intervals when there is a change in the system or network | Conducted annually when there are significant changes introduced into the system |
| ipconfig | ifconfig |
|---|---|
|
ipconfig (Internet Protocol Configuration) is a command used on Microsoft Windows to view and configure the network interface. |
ifconfig (Interface Configuration) command is used on Linux, Mac, and UNIX operating systems. |
|
This is a useful command for displaying all the TCP/IP network summary information currently available on a network. Additionally, it also helps in modifying the DHCP protocol and the DNS setting. |
This command is used to configure and control the TCP/IP network interface parameters from the Command Line Interface. It also allows you to view the IP addresses of these network interfaces. |
| Domain | Workgroup |
|---|---|
|
A domain is a centralized network model. |
A workgroup is a decentralized network model. |
|
Here, one administrator manages the domain and its resources. |
Here, every user manages the resources individually on their PCs. |
|
It is good for large networks. |
It is good for small networks. |
|
Here, the computer can be connected to any network. |
All the computers here should be connected to the same LAN. |
| Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) | Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) |
|---|---|
| HIDS is set up on a particular host/device and monitors the traffic of a particular device and suspicious system activities. | On the other hand, NIDS is set up on a network and is used to monitor the traffic of all network devices. |
| HIDS is used to detect intrusions. | NIDS is used for the network to monitor the traffic of all devices. |
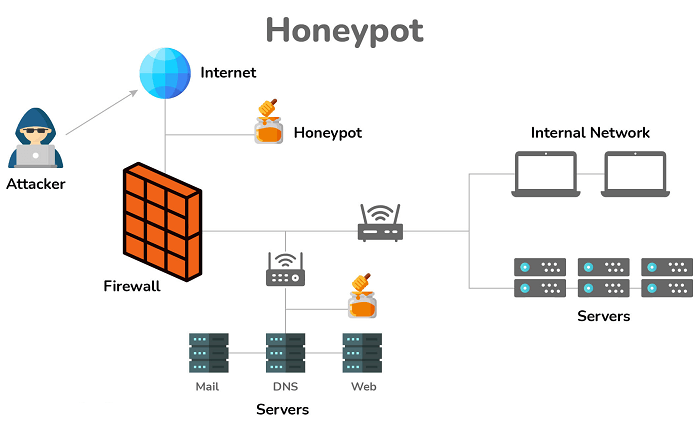
| Stored XSS Attacks | Reflected XSS Attacks |
|---|---|
| The attacks where the injected scripts are permanently stored on the target servers are called stored XSS attacks. | The attacks where the user has to send the request first, then start running on the victim's browser, are called reflected XSS attacks. |
| In stored XSS attacks, the victim retrieves the server's malicious script when requesting the stored information. | The reflected XSS attacks reflect results from the browser to the user who sent the request. |
| Black Box Testing | White Box Testing |
|---|---|
| It's a type of software testing in which the program's or software's internal structure is concealed. | It is a method of software testing in which the tester is familiar with the software's internal structure or code. |
| It is not necessary to have any prior experience with implementation. | It is not necessary to have prior experience with implementation. |
| On the basis of the requirement specifications paper, this testing can begin. | This form of software testing begins once the detailed design document has been completed. |
| It takes the least amount of time. | It takes the most amount of time. |
| It is the software's behavior testing. | It is the software's logic testing. |
| It is relevant to higher levels of software testing. | It is relevant to lower levels of software testing. |
| Block Cipher | Stream Cipher |
|---|---|
| By converting plaintext into ciphertext one block at a time, Block Cipher converts plain text into ciphertext. | Stream Cipher takes one byte of plain text at a time and converts it to ciphertext. |
| Either 64 bits or more than 64 bits are used in block ciphers. | 8 bits are used in stream ciphers. |
| The ECB (Electronic Code Book) and CBC (Common Block Cipher) algorithm modes are utilized in block cipher (Cipher Block Chaining). | CFB (Cipher Feedback) and OFB (Output Feedback) are the two algorithm types utilized in stream cipher (Output Feedback). |
| The Caesar cipher, polygram substitution cipher, and other transposition algorithms are used in the block cipher. | Stream cipher uses substitution techniques such as the rail-fence technique, columnar transposition technique, and others. |
| When compared to stream cipher, a block cipher is slower. | When compared to a block cipher, a stream cipher is slower. |
| VPN | VLAN |
|---|---|
| Helps to group workstations that are not within the same locations into the same broadcast domain | Related to remote access to the network of a company |
| Means to logically segregate networks without physically segregating them with various switches | Used to connect two points in a secured and encrypted tunnel |
| Saves the data from prying eyes while in transit and no one on the net can capture the packets and read the data | Does not involve any encryption technique but it is only used to slice up your logical network into different sections for the purpose of management and security |
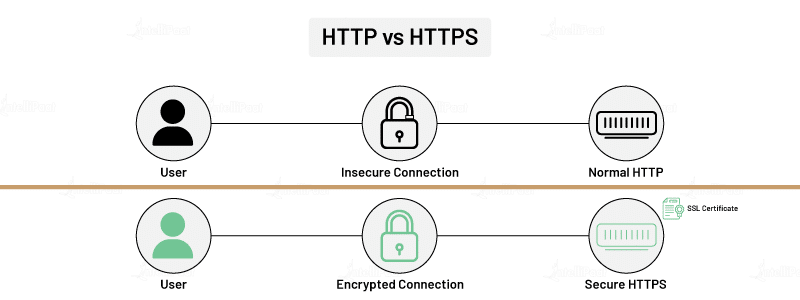
| Data Protection in Transit | Data Protection at Rest |
|---|---|
| Data is transmitted across devices or networks | Data is stored in databases, local hard drives, or USBs |
| Protects the data in transit with SSL and TLS | Protects the data at rest with firewalls, antiviruses, and good security practices |
| You must protect the data in transit since it can become vulnerable to MITM attacks, eavesdropping, etc. | You should protect the data at rest to avoid possible data breaches even when stolen or downloaded |