For most situations, DNS is concerned with a domain name being translated into the appropriate IP address. To learn how this process works, it helps to follow the path of a DNS lookup as it travels from a web browser, through the DNS lookup process, and back again. Let's take a look at the steps.
Note: Often DNS lookup information will be cached either locally inside the querying computer or remotely in the DNS infrastructure. There are typically 8 steps in a DNS lookup. When DNS information is cached, steps are skipped from the DNS lookup process which makes it quicker. The example below outlines all 8 steps when nothing is cached.
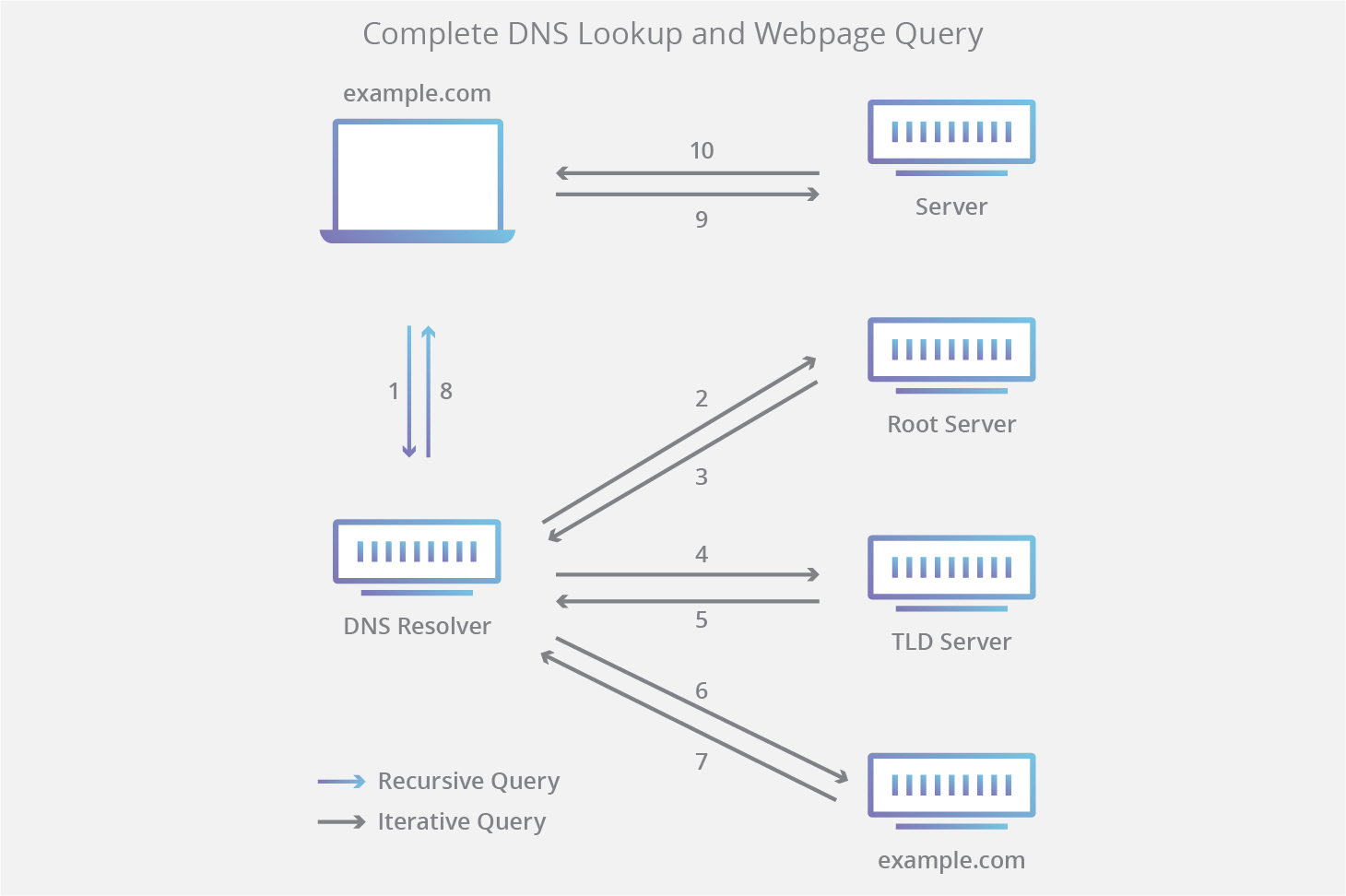
The 8 steps in a DNS lookup :
1. A user types ‘example.com’ into a web browser and the query travels into the Internet and is received by a DNS recursive resolver.
2. The resolver then queries a DNS root nameserver (.).
3. The root server then responds to the resolver with the address of a Top Level Domain (TLD) DNS server (such as .com or .net), which stores the information for its domains. When searching for example.com, our request is pointed toward the .com TLD.
4. The resolver then makes a request to the .com TLD.
5. The TLD server then responds with the IP address of the domain’s nameserver, example.com.
6. Lastly, the recursive resolver sends a query to the domain’s nameserver.
7. The IP address for example.com is then returned to the resolver from the nameserver.
8. The DNS resolver then responds to the web browser with the IP address of the domain requested initially.
Once the 8 steps of the DNS lookup have returned the IP address for example.com, the browser is able to make the request for the web page :
9. The browser makes a HTTP request to the IP address.
10. The server at that IP returns the webpage to be rendered in the browser (step 10).