| Aspect | Tableau | Power BI |
| Company and Licensing | Developed by Microsoft | Developed by Tableau Software (now part of Salesforce) |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly with a drag-and-drop interface | Steeper learning curve and requires more technical skills |
| Data Connectivity | Native connectors to Microsoft products and various data sources | Broad compatibility with databases, web services, and file formats |
| Visualization | Interactive visualizations and dashboards with modern design | Advanced visualization capabilities, complex charts and maps |
| Collaboration | Easy sharing within Power BI service, integration with SharePoint and Teams | Sharing options like Tableau Server and Tableau Online |
| Pricing Model | Free version (Power BI Desktop), Power BI Pro, Power BI Premium | Free trial (Tableau Desktop), Tableau Creator, Tableau Server |
| Power Query | Power Pivot |
| Power Query is all about analyzing data. | Power Pivot is all about getting and Transforming data. |
| Power Query is an ETL service tool. | Power Pivot is an in-memory data modeling component |
| Managed Enterprise BI | Self-service BI |
|---|---|
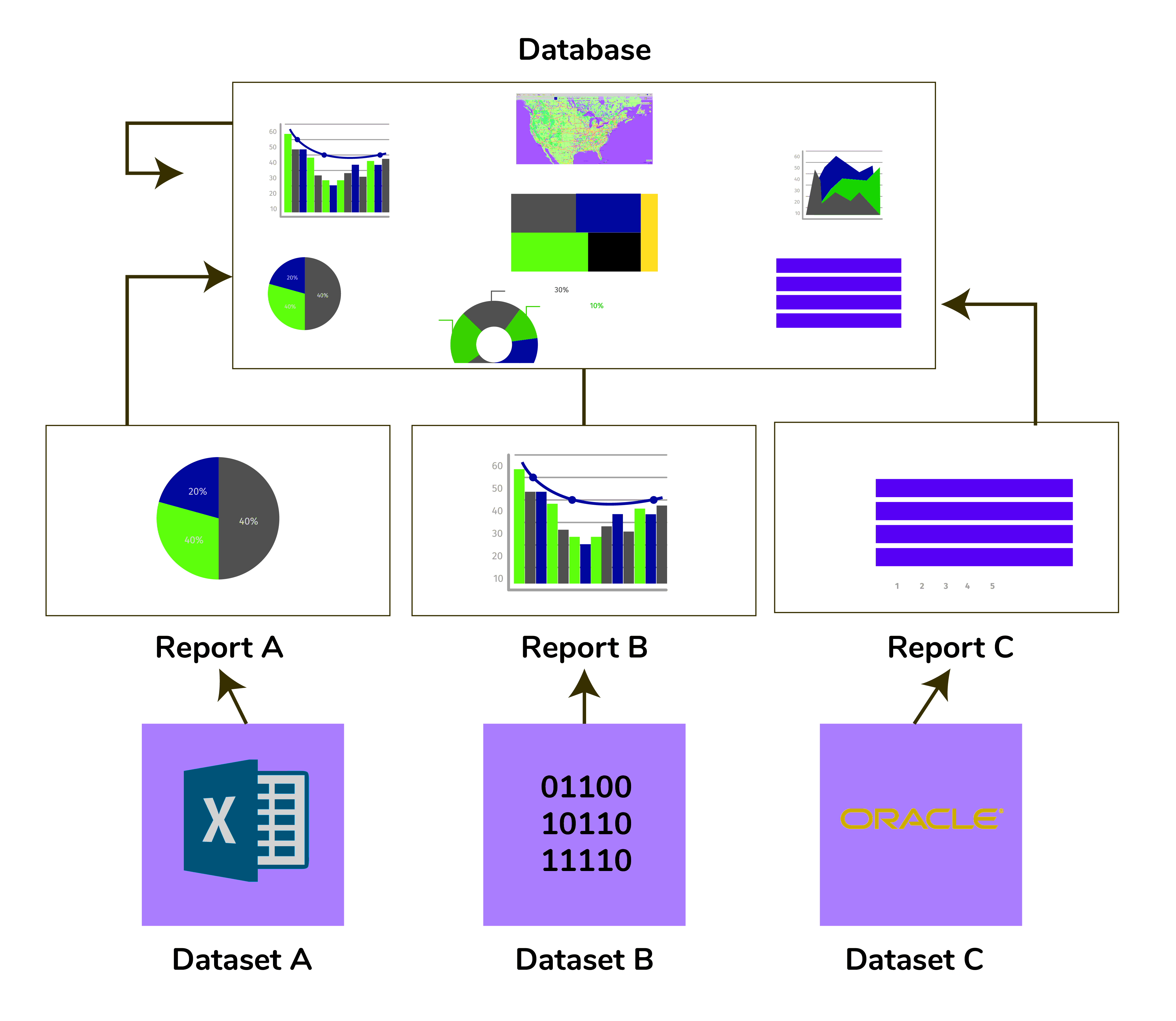
| Here, data flows in from a plethora of sources and, for this reason, there is no order in which companies ingest and manage their data sources. | This enables companies to ingest data from any data source, seamlessly. Companies take in data from any source in any format. |
| Companies fail to conduct their business operations, effectively, as they are not able to report and analyze data and collaborate for collecting valuable insights from it. | With data ingestion falling into order, companies are able to process data and, consequently, conduct business operations with ease. |
| There are time constraints and a lack of proper information when it comes to analyzing data. | Analyzing data is easy, and it is done implicitly. Time constraints are hence alleviated. |
| Third-party vendors are employed to help companies make the most out of their data sources, leading to budget problems and slow productivity. | There is no need for third-party vendors anymore and all associated constraints are eradicated. |
| Complex programming skills are necessary for generating reports. | Users could generate intuitive and actionable dashboards almost instantaneously without executing complex programming codes. |
let dataSource = powerbi.data.createDataSource({
type: "sql",
connectionString: "Server=<serverName>;Database=<databaseName>;Trusted_Connection=True;",
table: "Sales"
});
powerbi.datasets.createDataset({
dataSource: dataSource,
tables: [{ name: "Sales", columns: [{ name: "Product", type: "string" }, { name: "Amount", type: "decimal" }] }]
})
.then(function (dataset) {
let report = powerbi.report({
data: dataset,
type: "pie",
options: {
dataLabels: {
fontSize: 20
},
legend: {
visible: false
}
}
});
powerbi.render(document.getElementById("container"), report);
});
| Parameter | Power BI | Excel |
| Tabular reports | Power BI is not so handy for tabular style reports | Excel is better at handling tabular-style reports. |
| Duplicate Table | Cannot display duplicated tables | Allows to display duplicated tables |
| Reports | Offers beautiful, personalized, and interactive reports | Doesn’t offer advanced cross-filtering between charts. |
| Cross filtering | Offers advanced features in cross-filtering between charts. | Doesn’t offer advanced cross-filtering between charts. |
| Analytics | Offers simple analytics | Offers high-level analytics |
| Applications | Ideal for dashboards, KPIs, alerts, and visualizations, including analysing your data visually. | Excel does have some new charts now, and they can’t connect to the data model. |
 A: Name of the project
A: Name of the projectlet myData = [
{ year: 2020, sales: 5000 },
{ year: 2021, sales: 6000 },
{ year: 2022, sales: 7000 }
];
powerbi.connect({
data: myData,
type: "column",
options: {
dataLabels: {
fontSize: 20
},
legend: {
visible: false
}
},
error: function(error) {
console.error("Data connection error:", error);
}
});
In this example, the error function is used to catch any errors that occur when connecting to the data source. This can help you diagnose and resolve any issues you encounter with your data connection.
.xlsx, .xlxm), Power BI Desktop files (.pbix) and Comma-Separated Values (.csv). statewith() function returns the logical answers TRUE if the sub-string is the starting string for the superstring. If it is not, it will return false.
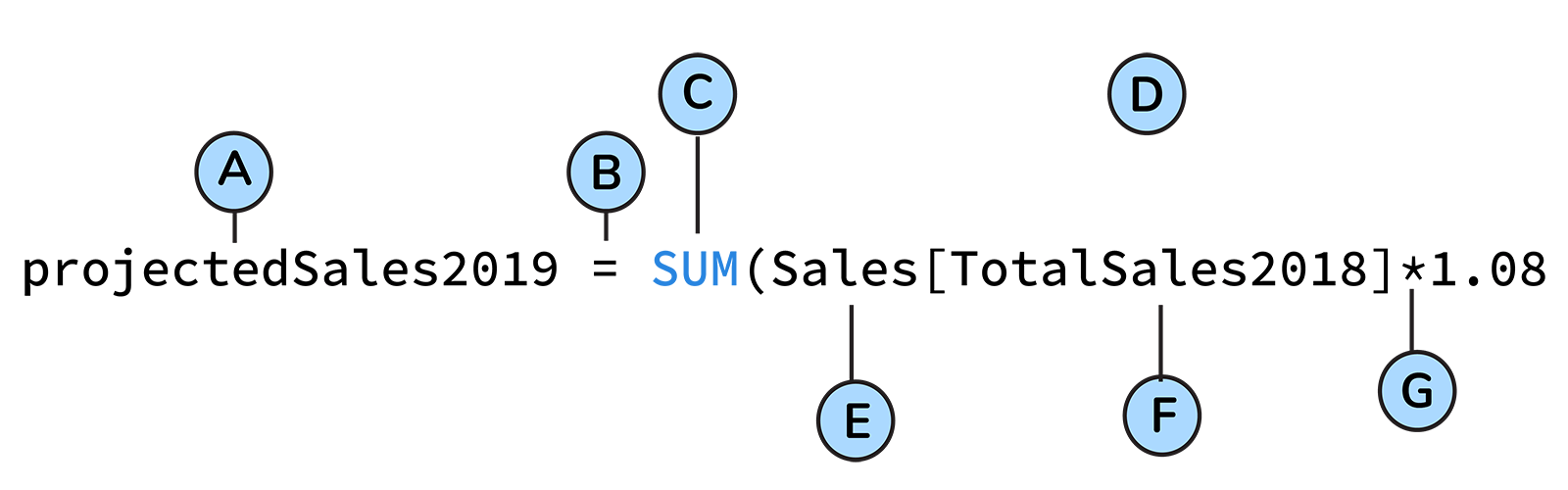
Average Sales per Customer = SUM(Orders[Sales]) / COUNT(Orders[CustomerID])​library(dplyr)
library(tidyverse)
data("mtcars")​fit <- lm(mpg ~ wt, data = mtcars)​ggplot(mtcars, aes(x = wt, y = mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)​<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://microsoft.github.io/PowerBI-JavaScript/demo/node_modules/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://microsoft.github.io/PowerBI-JavaScript/demo/node_modules/powerbi-client/dist/powerbi.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="reportContainer"></div>
<script>
var models = window['powerbi-client'].models;
var embedConfig = {
type: 'report',
tokenType: models.TokenType.Embed,
accessToken: 'ACCESS_TOKEN',
embedUrl: 'EMBED_URL',
id: 'REPORT_ID',
settings: {
filterPaneEnabled: false,
navContentPaneEnabled: false
}
};
var $reportContainer = $('#reportContainer');
var report = powerbi.embed($reportContainer.get(0), embedConfig);
</script>
</body>
</html>​embedConfig object defines the report to be embedded, including the access token, embed URL, report ID, and display settings. The powerbi.embed method is then used to embed the report into a container element on the page, which is identified by the $reportContainer variable. | Calculated Columns | Calculated Tables | Measures |
| Added to tables by applying DAX formula on the existing data | Created using DAX formula to define values | Use other DAX functions to create complex calculations |
| DAX formula defines values in new columns rather than querying data sources | Created in both Report and Data views | Used for highlighting running totals, comparing sales, sales forecasting, and other purposes |
| Useful when data sources do not contain data presented in the desired format | Work well for intermediate calculations and the data that users want to be stored in the model | Created in both Report and Data views |
CALCULATE ( [, [, [, … ]]] )​Distinct() and Values() functions are the same in Power BI. The only difference between them is that the Values() function don't calculate null values, whereas the Distinct() function calculates even the null values.
CORR() is a correlation function used to provide a correlation between two distinct variables ranging from -1 to 1.
library(ggplot2)
library(powerBIVisuals)
powerBIBar <- function(data, visualArgs) {
p <- ggplot(data, aes(x = data$x, y = data$y)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity")
powerBIVisual(p, visualArgs)
}​library(devtools)
# Create a folder for your custom visual
create("myCustomVisual")
# Copy the code for your custom visual into a file called myCustomVisual.R
# Create a file called DESCRIPTION with the following content
Package: myCustomVisual
Type: Package
Title: My Custom Visual
Version: 0.0.1
Authors@R: person("Your Name", email = "your.email@example.com")
# Build the package
build()​