Search engines have a number of computer programs called web crawlers (thus the word Crawling), that are responsible for finding information that is publicly available on the Internet.
Search engines have their own crawlers, small bots that scan websites on the world wide web. These little bots scan all sections, folders, subpages, content, images, videos or any other format (CSS, HTML, javascript, etc) everything they can find on the website.
Crawling is based on finding hypertext links that refer to other websites. By parsing these links, the bots are able to recursively find new sources to crawl.
There are a number of things to do to make sure that crawlers can discover and access your website in the fastest possible way without problems.
1. Use Robots.txt to specify which pages of your website you don’t want crawlers to access.
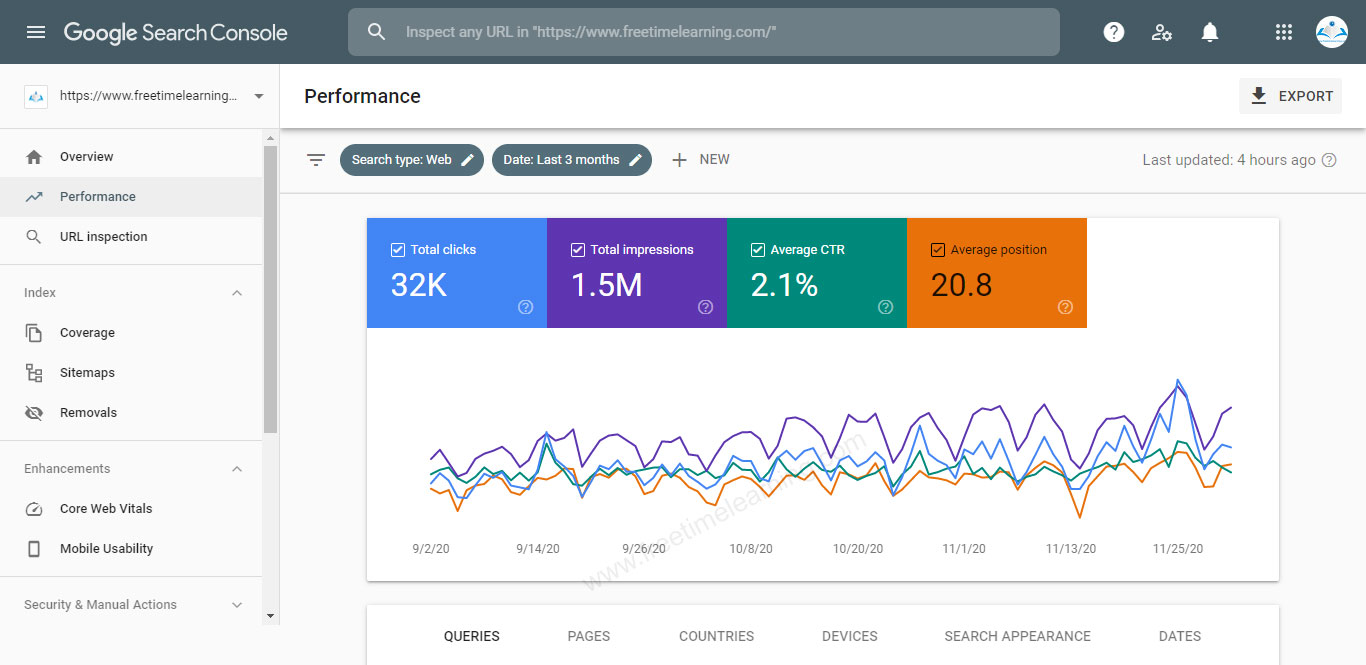
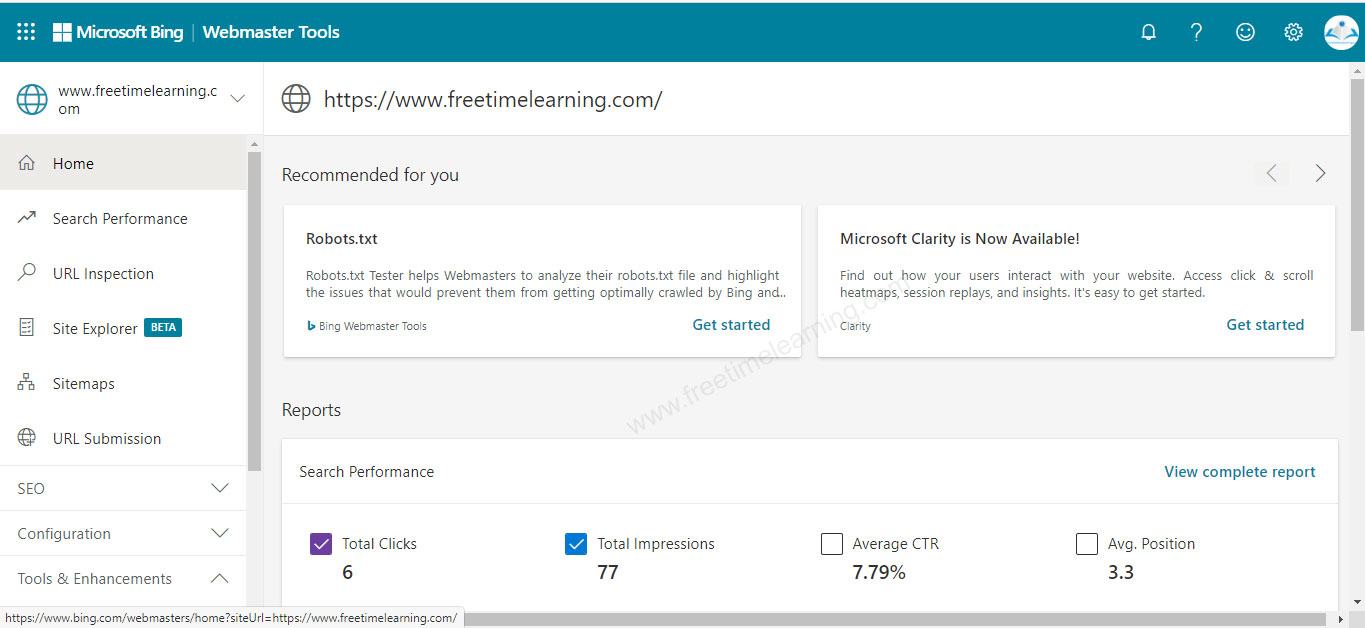
2. Top search engines like Google and Bing, have tools (Webmaster tools), you can use to give them more information about your website (number of pages, structure, etc) so that they don’t have to find it themselves.
3. Use an XML sitemap to list all important pages of your website so that the crawlers can know which pages to monitor for changes and which to ignore.
Google Webmaster Tools Example:
Big Webmaster Tools Example:
Search engines process and store information they find in an index, a huge database of all the content they’ve discovered and deem good enough to serve up to searchers. Once the bots crawl the data, it’s time for indexing. The index is basically an online library of websites.
Your website has to be indexed in order to be displayed in the search engine results page. Keep in mind that indexing is a constant process. Crawlers come back to each website to detect new data.
When someone performs a search, search engines scour their index for highly relevant content and then orders that content in the hopes of solving the searcher's query. This ordering of search results by relevance is known as ranking. In general, you can assume that the higher a website is ranked, the more relevant the search engine believes that site is to the query.